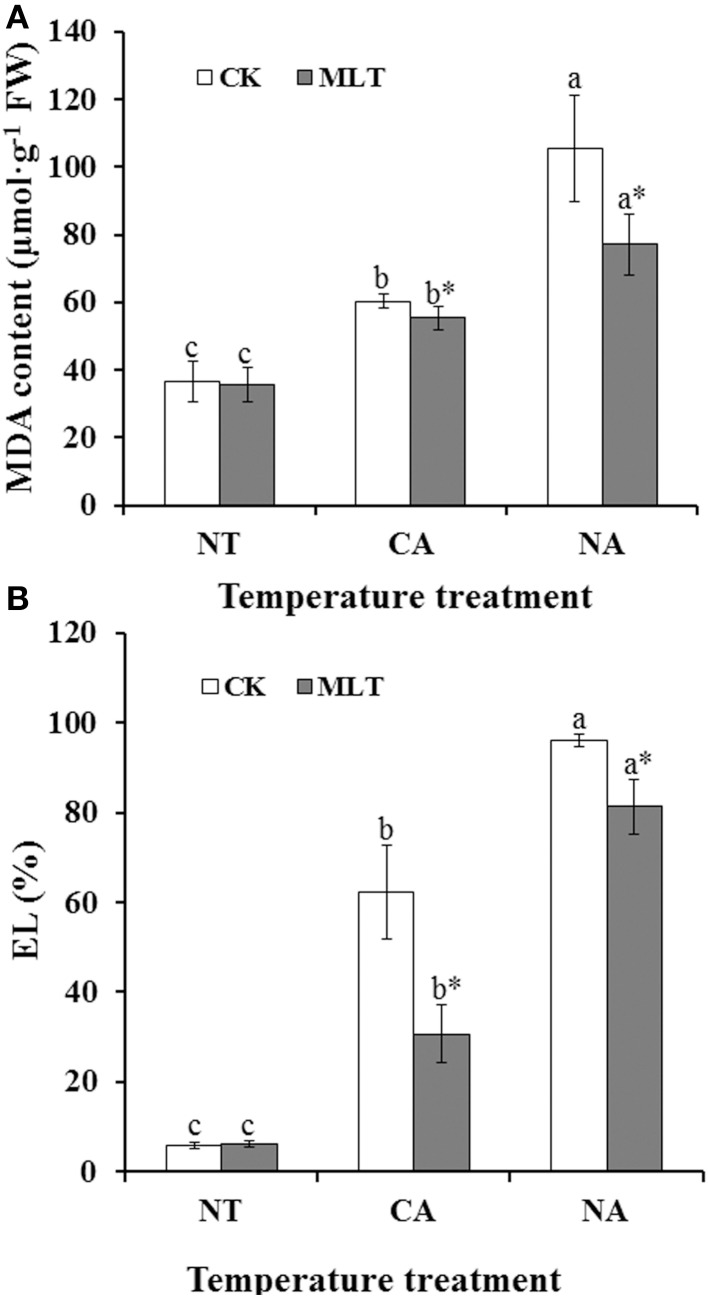
Figure 1.
Alteration of cell membrane stability and lipid peroxidation in the leaves of bermudagrass after 100 μM melatonin treatment under cold stress. (A) Malonaldehyde (MDA) content; (B) electrolyte leakage (EL). Experiment included five repeats of each treatment, and means were average values of MDA content and EL, respectively. Independent-samples t-test was used to determine statistical differences. Bars show standard deviation. Columns marked with different letters indicate statistical difference significance at P < 0.05 among the temperature treatments. Column marked with asterisk was significantly different after MLT treatment. NT was normal temperature of 30°C. CA was cold acclimation, during which Bermudagrass was treated with 4°C for 7 d and then transferred to −5°C for 8 h. NA was cold stress without acclimation, in which plants were treated with −5°C for 8 h without pre-treatment with 4°C. CK was control (treated without melatonin). MLT, melatonin; FW, fresh weight.