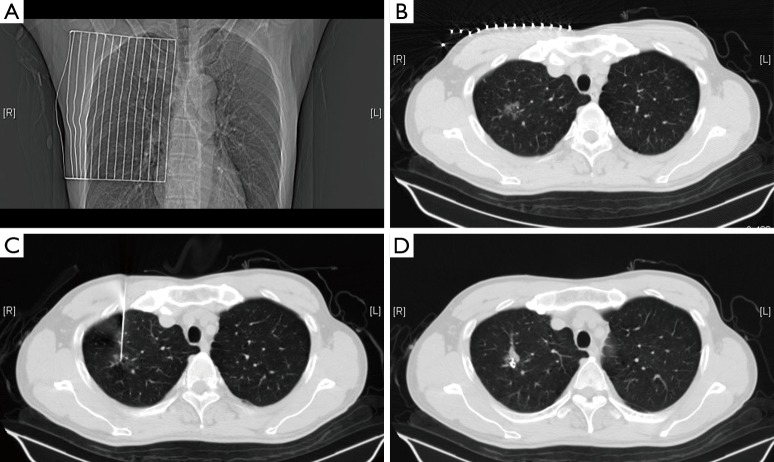
Figure 1.
(A) The ruler is placed on the surface of the chest wall; (B) the depth and angle of the needle insertion is measured according to the location of focal ground-glass opacities (fGGOs) guided by computed tomography (CT); (C) the needle is inserted along the optimal path closest to the lesion; (D) the stylet is removed, the coil is placed, and the patient is assessed for any serious complications.