Figure 7.
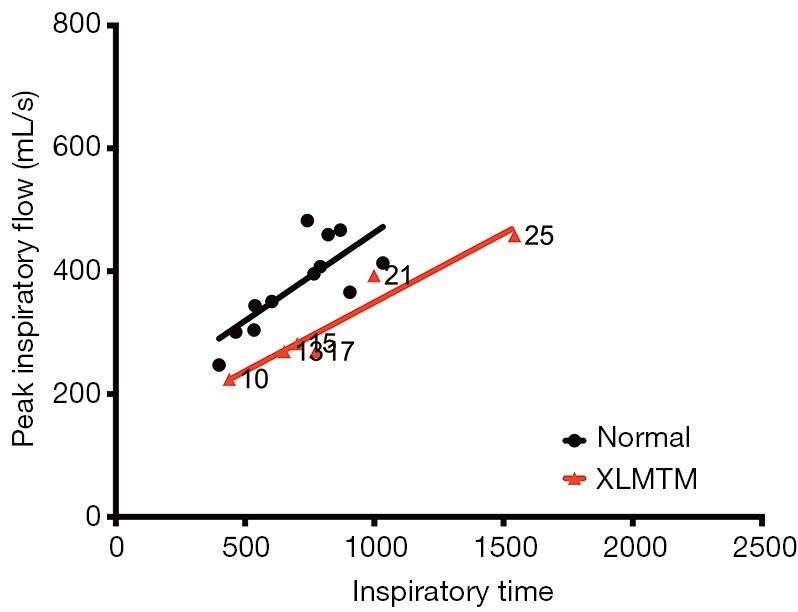
XLMTM dogs increase inspiratory time with a concomitant decrease in volume of inspiratory flow to maintain respiratory homeostasis. Peak inspiratory flow against inspiratory time, with associated linear regression, for controls (black) and XLMTM dogs (red) measured over time. Weeks-of-age at the time of measurement are indicated on the graph for affected animals. XLMTM, X-linked myotubular myopathy.
