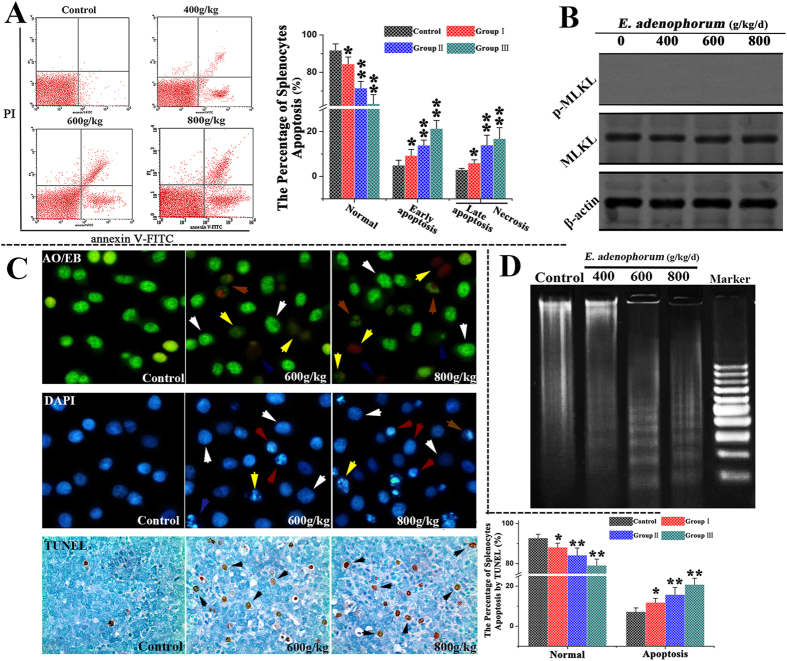
Figure 2. E. adenophorum administration induces apoptosis in splenocytes.
(A) Scattergram of apoptotic splenocytes. The splenocytes were analyzed for apoptosis through flow cytometry based on Annexin V and PI staining.The percentage of splenocyte apoptosis(%). E. adenophorum significantly induced apoptosis in splenocytes. (B) MLKL and p-MLKL protein levels were measured to detect programmed necrotic cell death through western blot analysis. (C) Detection of apoptotic splenocytes through DAPI and AO/EB staining and TUNEL assays. Representative spleen sections from Saanen goats were analyzed in TUNEL assays to detect apoptotic cell death. The number of TUNEL-positive cells (black indicated arrows) in the spleen was counted from five random microscopic fields. Magnification, 400×. Nuclear morphological changes in splenocytes were observed using a fluorescence microscope after DAPI (200×) and AO/EB staining (400×). Normal cells(white arrow), early apoptosis(red arrow), late apoptosis(yellow arrow), and necrosis (blue arrow). (D) Induction of DNA fragmentation. DNA isolated from E. adenophorum-treated splenocytes was subjected to 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, followed by the visualization of bands and photography. The data are presented as the means ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared with the control group.