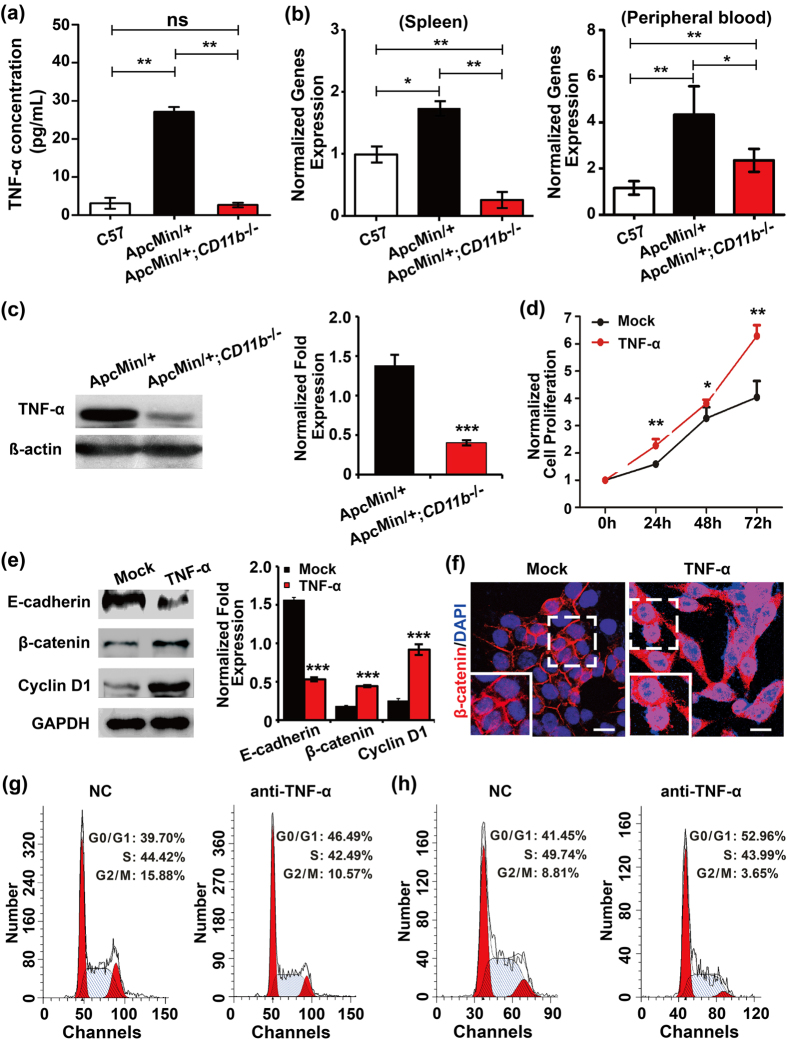
Figure 4. CD11b deficiency inhibits tumor growth by suppressing TNF-α release.
The concentration of TNF-α in the peripheral blood of the C57, ApcMin/+ and ApcMin/+;CD11b−/− mice was examined by ELISA (a). The mRNA level of TNF-α in the peripheral blood and spleen of the C57, ApcMin/+ and ApcMin/+;CD11b−/− mice was examined by qRT-PCR (b). The proteins expression of TNF-α in the tumor tissues from the ApcMin/+ and ApcMin/+; CD11b−/− mice was examined by immunoblotting (c). The protein band intensities were quantitated and normalized to those of GAPDH. TNF-α can significantly promoted cell proliferation (d) and Wnt/β-catenin activation (e) in HCT-116 cells (this cell line shows low Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity). TNF-α can also induce the nuclear translocation of β-catenin in HCT-116 cells (f), Scale bar: 25 μm. All results represent at least three separate experiments (d–f). Inhibit TNF-α arrested CT-26 cells (g) and HCT-116 cells (h) at the G1/S transition in myeloid cell and tumor cell co-culture system. The results are expressed as the means ± S.D. ns: P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.