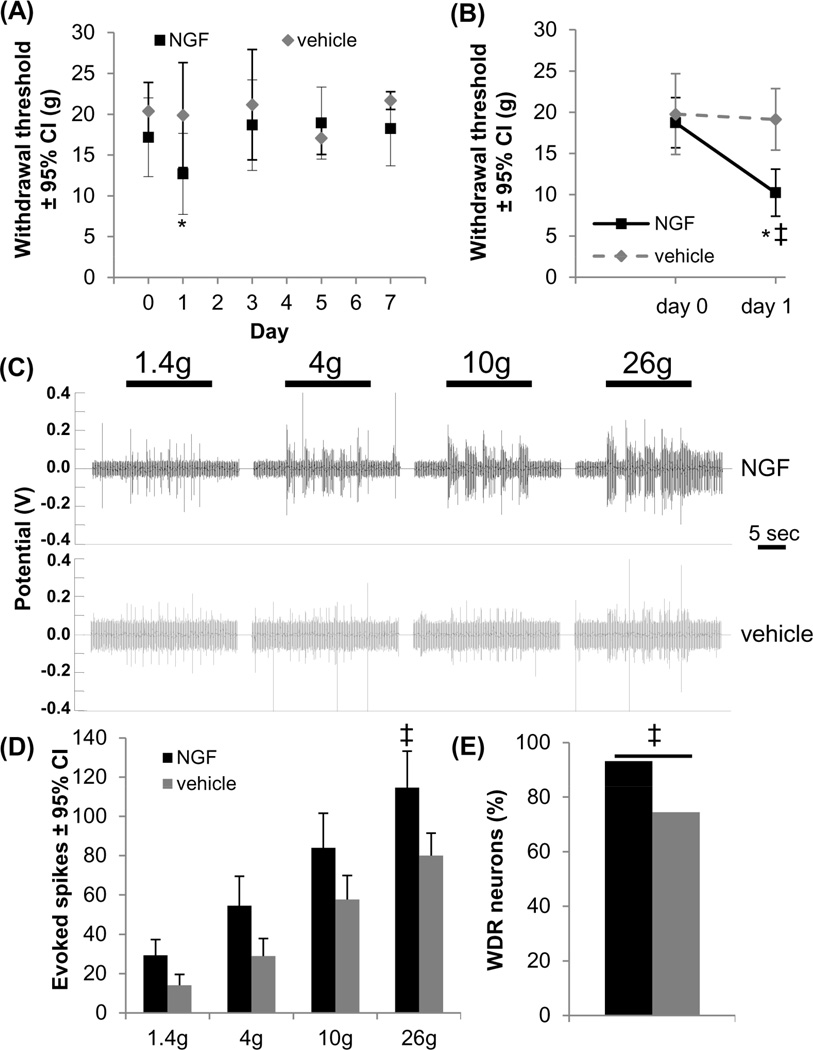
Figure 4.
Intra-articular NGF induced transient behavioral sensitivity that was associated with spinal neuronal hyperexcitability. (A) Intra-articular NGF significantly reduced the withdrawal threshold from baseline at day 1 (*p<0.010), but it returned to baseline by day 3. Injection of PBS vehicle did not alter the withdrawal threshold from baseline at any day. (B) At 1 day after intra-articular NGF the withdrawal threshold significantly decreased relative to baseline (*p<0.001) and to vehicle injection (‡p<0.001). (C) Representative extracellular recordings in the spinal cord at day 1 demonstrated increased evoked neuronal firing after NGF. (D) The number of evoked spikes significantly increased (‡p<0.040) for the noxious 26g filament after NGF injection. (E) Intra-articular NGF increased the number of spinal neurons classified as WDR neurons compared to the number identified after intra-articular vehicle administration (‡p=0.016). NGF: nerve growth factor; WDR: wide dynamic range.