Fig. 4.
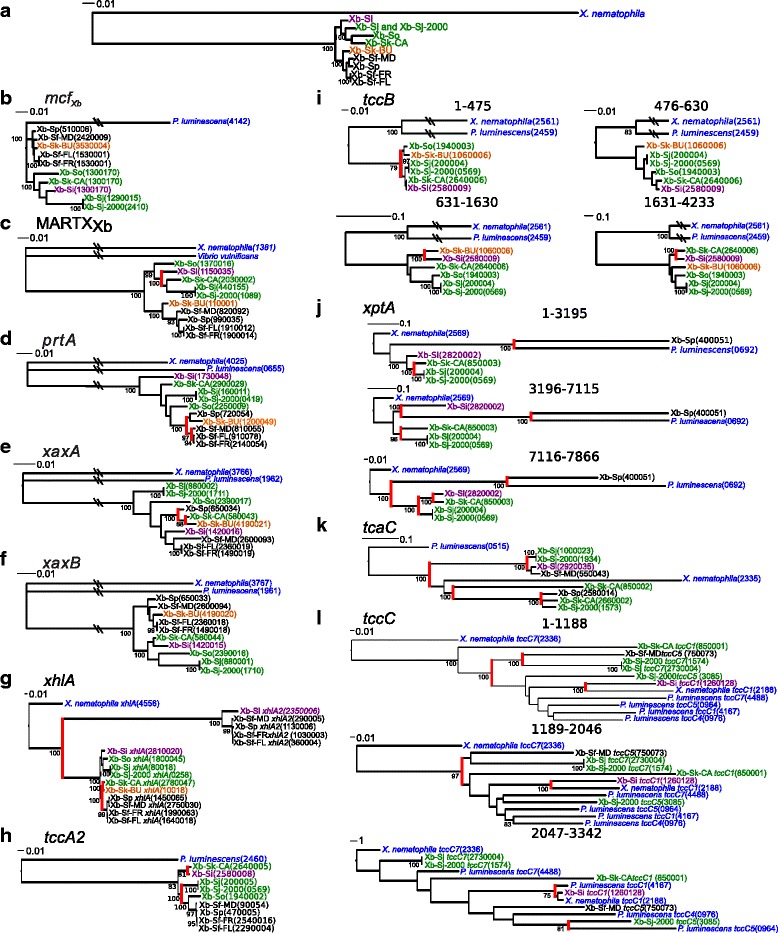
Phylogenies of partitioned nucleic acid sequence. The nucleic acid sequences of genes were analyzed for recombination, and for each piece, phylogenies were built. The gene phylogenies were compared to the whole genome phylogeny of the bacterial strains (a) [5]. Shown above are the trees for X. bovienii genes mcf Xb (b), MARTX Xb (c), prtA (d), xaxA (e), xaxB (f), xhlA (g), tccA2 (h), tccB2 (i), xptA2 (j), tcaC (k), and tccC (l). Values indicate bootstrap values. The leaves are color-coded by clade determination from the core X. bovienii phylogeny, and red highlighting indicates strongly supported branches in the gene tree that do not match the previously reported bacterial phylogeny [5]
