Fig. 2.
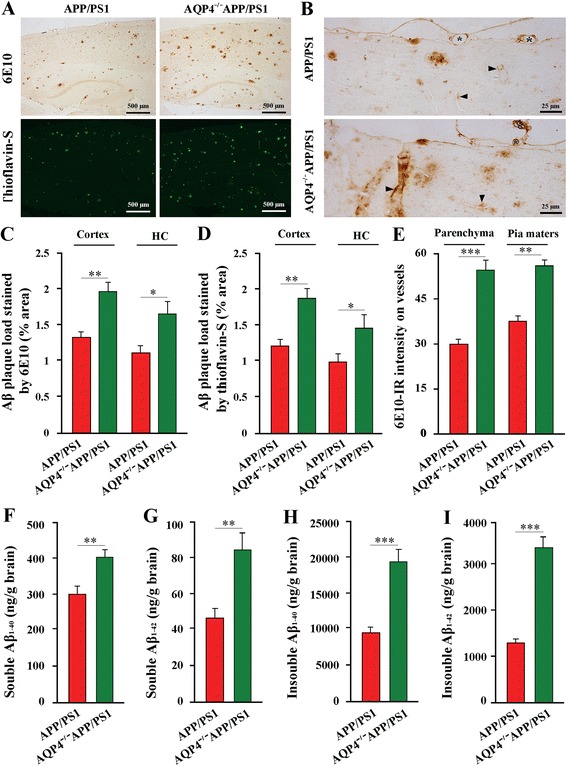
AQP4 deficiency increased brain Aβ accumulation and CAA in 12 month-old APP/PS1 mice. a Aβ deposition in the hippocampus and cortex stained by 6E10 and Thioflavin-S. b High magnification micrographs of 6E10 immunostaining. There was increased amyloid deposition along small and large vessels in the brain parenchyma (arrowheads) and leptomeningeal vessels (stars) of AQP4−/−APP/PS1 mice, compared to APP/PS1 controls. c The area percentage of 6E10-positive Aβ plaque load in the hippocampus (HC) and cerebral cortex. d The area percentage of Thioflavin-S-positive Aβ plaque load in the hippocampus (HC) and cerebral cortex. e 6E10-immunoreactive (IR) intensity on the cortical vessels and leptomeningeal vessels. f-i ELISA analysis of soluble and insoluble Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 in the brain samples. Data represent mean ± SEM from 5 to 6 mice (3–4 female, and 1–2 male) per group. The statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
