Figure 1. Common epigenetic modifications.
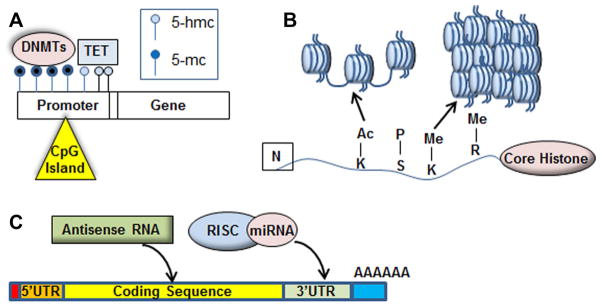
(A) DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) modify CpG islands, which are found primarily in the promoter region of genes, with 5-methylcytosine (5-mC). An increase in promoter methylation (dark blue circles) results in reduced gene expression, while TET enzyme modification of 5-mC to 5-hmC results in de-repression of gene expression. (B) The four core histones undergo amino acid-specific acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation. The post-translational modifications result in either the relaxation of the nucleosome structure (euchromatin), which allows transcription factor access to genes, or causes nucleosomes to tighten into heterochromatin, blocking transcription at specific loci. (C) Post-transcription factors including microRNAs, antisense RNA, and long non-coding RNA act at promoter regions, coding regions, and 3′UTR seed sequences to regulate the expression of target mRNAs.
