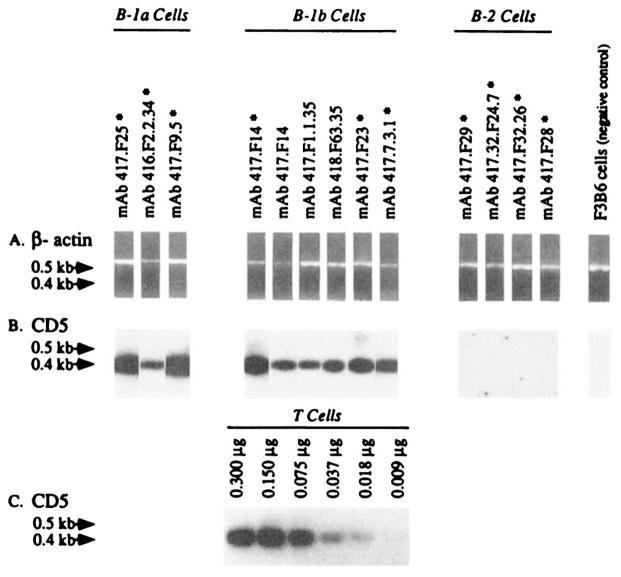
FIGURE 1.
Expression of CD5 mRNA by the B-1a, B-1b, and B-2 cell-derived mAb-producing lines. Poly(A)+ RNA (0.300 μg) extracted from mAb-producing EBV-transformed cell lines (asterisks), mAb-producing EBV-transformed somatic cell hybrid lines, freshly isolated T cells, or from the human-mouse heterohybridoma F3B6 cells, were individually reverse transcribed. The cDNA was individually amplified by PCR using β-actin-specific or CD5-specific oligonucleotide primers and fractionated on a 1.2% agarose gel (see Materials and Methods). A, Ethidium bromide-stained gel containing amplified β-actin DNA (~0.6 kb); B, Hybridization of the 32P-labeled “internal” CD5-specific oligonucleotide probe with fractionated CD5 DNA amplified from cDNA reverse transcribed from the mAb-producing cell lines or the fusion partner F3B6 cells; C, hybridization of the 32P-labeled “internal” CD5-specific oligonucleotide probe with fractionated CD5 DNA amplified from cDNA individually reverse transcribed from different amounts (0.009 to 0.300 μg) of purified T cell mRNA.