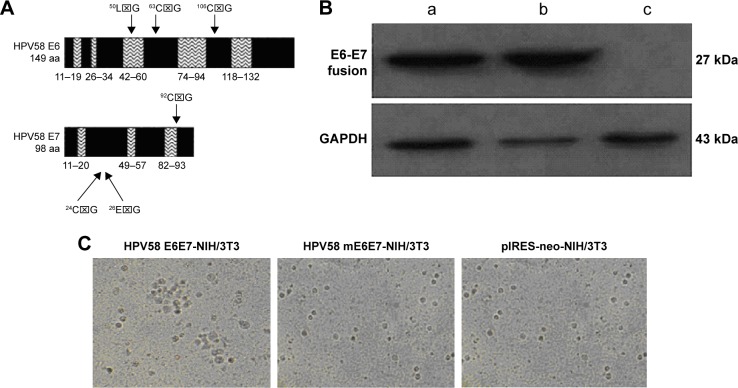
Figure 2.
Gene changes used to inactivate the oncogene function of HPV58 E6E7.
Notes: (A) Locations of the point mutations introduced into the HPV58 E6 and E7 proteins. The naturally occurring amino acids E6-50L, 63C, and 106C and E7-24C, 26E, and 92C were mutated to glycine. (B) Western blot analysis showed that HPV58 E6E7 and HPV58 mE6E7 fusion proteins can be expressed in NIH/3T3-HPV58 E6E7 (a) and NIH/3T3-HPV58 mE6E7 (b) cells, but not in NIH/3T3-neo cells (c). GAPDH served as a protein loading control. (C) Colony formation in soft agar about three stable transfected NIH/3T3 cell lines.
Abbreviations: HPV, human papillomavirus; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ⌧, TTA(L)- Leucine, TGT(C)-Cysteine, GGT(G)-Glycine, TGC(C)-Cysteine, GAG(E)-Glutamic acid, GGC(G)-Glycine, GGG(G)-Glycine.