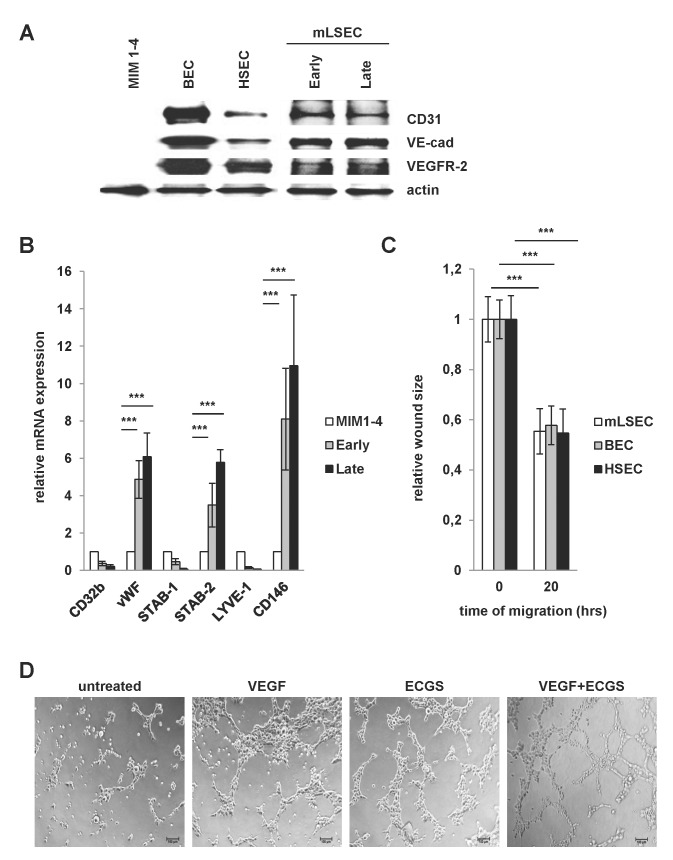
Fig 2. Endothelial integrity of mLSECs.
(A) Western blot analysis of early and late passaged mLSECs using anti-CD31, anti-VE-cadherin and anti-VEGFR-2 antibodies. The EC phenotype of mLSECs were compared to blood endothelial cells (BECs) and hHSECs. Immortalized p19ARF-deficient hepatocytes, termed MIM1-4, were used as a negative control. Actin is shown as a loading control. (B) qPCR analyses of Stab-1, Stab-2, vWF, Lyve-1, CD32b and CD146 in mLSECs. MIM1-4 cells served as a negative control. RhoA was used as a housekeeping gene. (C) Migratory abilities of mLSECs, BECs and HSECs as shown by wound healing assay in medium containing ECGS. Quantification of phase contrast images of cells after wounding (0 hours) and after wound closure (20 hours). (D) Tube formation of mLSECs as detected after cytokine stimulation.