Fig. 2.
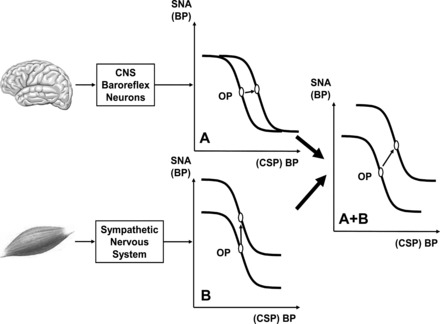
Hypothetical stimulus-response curves for arterial baroreflex, expressed as relationship between sympathetic nervous activity (SNA) and systemic BP or often in experiments as relationship between BP and isolated carotid sinus pressure (CSP). Operating point (OP) is BP “sought” by arterial baroreflex (often point of maximal gain). A: resetting of baroreflex by central command, a stimulus acting on neuron pool receiving baroreceptor afferent. OP is shifted laterally to a higher BP. CNS, central nervous system. B: vertical shift of baroreflex function curve by muscle chemoreflex, a stimulus that increases SNA and raises BP without changing OP; i.e., influence is confined to efferent arm of baroreflex. A + B: hypothetical combined effects of both stimuli on curve during exercise (upward and rightward resetting). Modified from Fig. 4 in Rowell and O'Leary (95).
