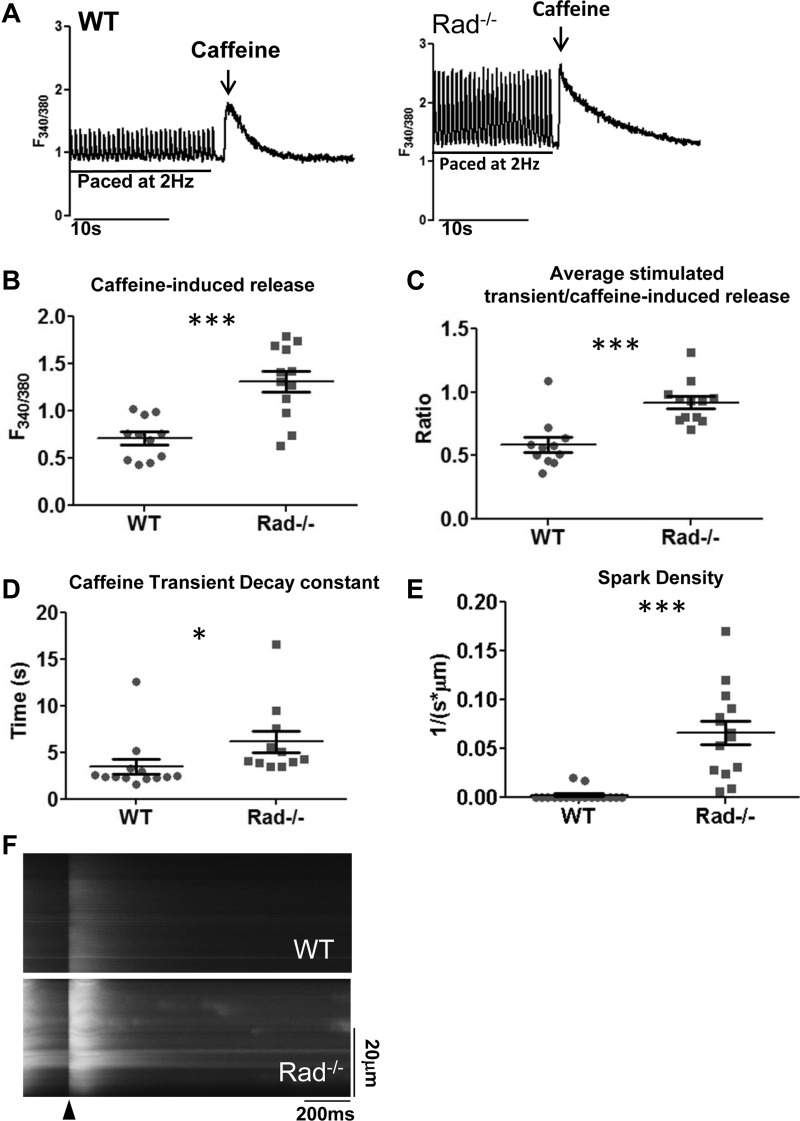
Fig. 6.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) load is elevated in Rad−/−. A: representative paced and caffeine-stimulated Ca2+ transients from WT and Rad−/−. B and C: caffeine-induced Ca2+-release amplitude (B) and the ratio of stimulated calcium release to total caffeine-induced SR Ca2+ release (C) was greater in Rad−/− compared with WT. D: caffeine decay constant (tau, τ) is significantly prolonged in Ca2+-free media. E: spark frequency is increased in Rad−/− compared with WT. F: representative line scan showing stimulus (arrowhead) and sparks measured after a >e-fold decay of the global Ca2+ transient in WT and Rad−/−; n = 3 mice per genotype. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs. WT.