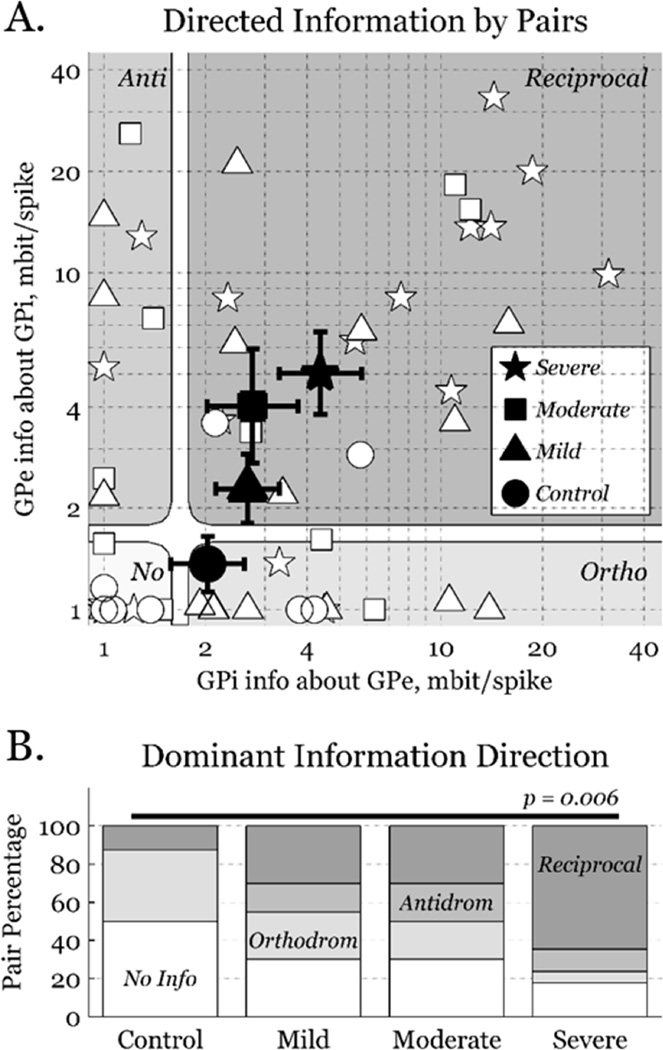
Figure 4.
Bidirectional information. A) A marker (white) for each recorded pair, where the shape denotes the parkinsonian condition. Large markers (black) indicate geometric mean±sem for each condition, as is natural for this logarithmic representation. Information greater than one-half of a standard deviation was considered significant (1.9 mbit per spike). Connections are divided into 4 classes by information direction: no information, orthodromic, antidromic, and reciprocal. B) Distributions of information direction for the four conditions. Uninformative (white) and orthodromic (light grey) pairs decrease, while reciprocal (dark grey) pairs increase, with parkinsonian severity.