Figure 4.
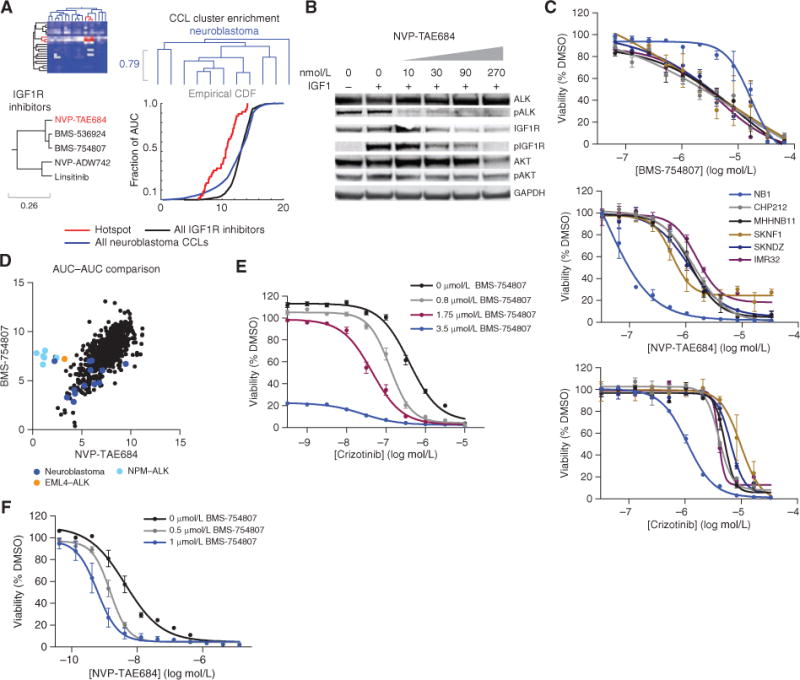
ACME analysis associates the sensitivity of neuroblastoma CCLs to IGF1R inhibitors to reveal the exquisite sensitivity of ALK-overexpressed neuroblastoma CCLs to dual IGF1R and ALK inhibition. A, the three enrichments for IGF1R inhibitors and neuroblastoma CCLs: row and column dendrograms and empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the AUC distributions. The purity of the compound cluster is 0.8 and the confdence is 1. The purity of the CCL cluster is 0.55 and the confdence is 0.43. On the compound dendrogram segment, IGF1R inhibitors (black) and NVP-TAE684 (inhibiting ALK; red) are depicted. B, Western blot of lysates from NB1 cells that were serum-starved overnight, followed by 3-hour treatment with NVP-TAE684 at the indicated concentrations, and then 10-minute stimulation with IGF1. Experiments were repeated twice. These data confrm loss of phophorylated (p) IGF1R upon treatment with NVP-TAE684. C, confrmation of profling results for BMS-754807, crizotinib, and NVP-TAE684. The average of two replicates from two independent experiments is shown. D, AUC-AUC comparison for NVP-TAE684 and BMS-754807 with neuroblastoma CCLs (dark blue), CCLs with NPM-ALK rearrangement (light blue), and EML4-ALK rearrangements (orange) highlighted. E, sensitization of crizotinib by cotreatment with BMS-754807. Two independent experiments were performed. The average of one experiment with 5 to 7 replicates is shown. F, sensitization of NVP-TAE684 by cotreatment with BMS-754807. Two independent experiments were performed. The average of one experiment with 5 to 7 replicates is shown.
