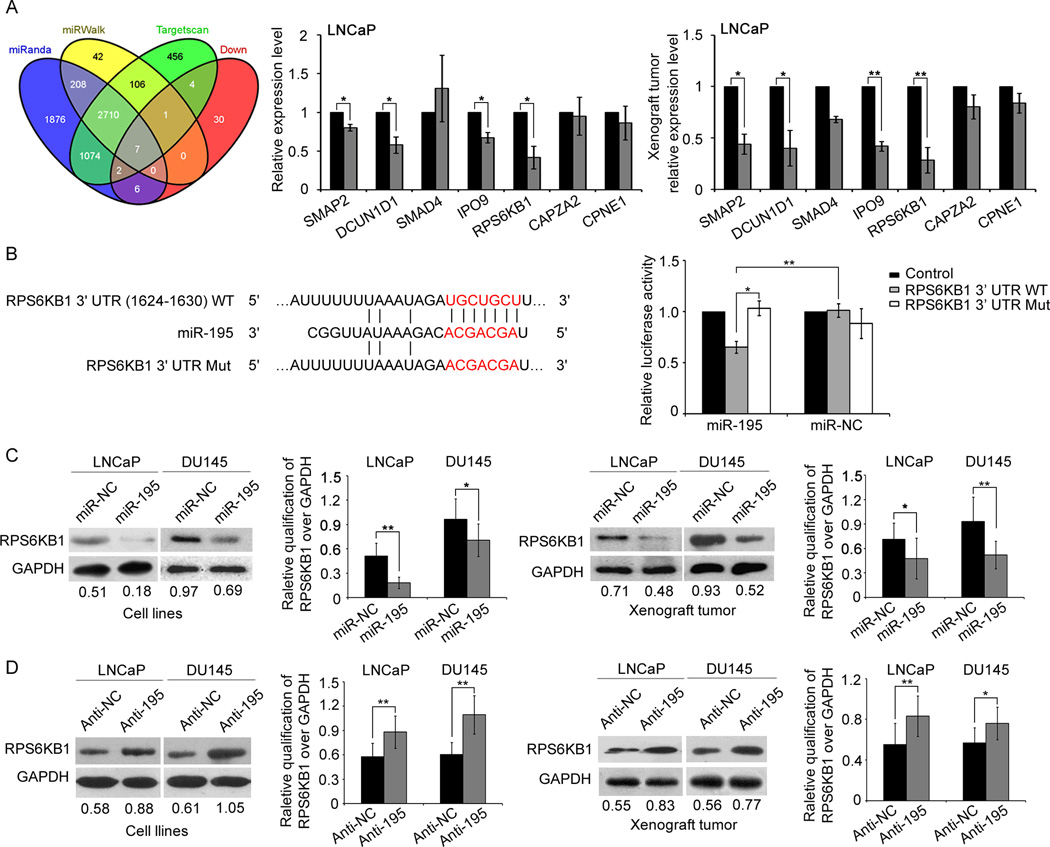
Fig. 4. miR-195 downregulates RPS6KB1 expression by directly targeting its 3′-UTR.
(A). Overlap of three miRNA target bioinformatic prediction methods and miR-195-induced down-regulated proteins. qRT-PCR analysis shown that the endogenous SMAP2, RPS6KB1, IPO9 and DCUN1D1 expression in cells and established tumors associated with LNCaP cells stably expressing miR-195 were all significantly reduced at mRNA levels. Data were presented as Mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (B). RNA sequence alignment showing the 3'-UTR of RPS6KB1 mRNA contains a complementary site for the seed region of miR-195. RPS6KB1 mut is a mutant with substitutions in the complementary region as a negative control. Dual luciferase reporter assay was performed to confirm the miR-195 binding target. The luciferase activity was detected after transfection of psiCHECK-2 luciferase reporter vector (psiCHECK-2-RPS6KB1-3’UTR-WT or psiCHECK-2-RPS6KB1-3’UTR-MUT) into the miR-195 or miR-NC transfected LNCaP cells. Data were presented as Mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (C). Enforced expression of miR-195 suppressed the expression of RPS6KB1 protein in both PCa cell lines and the corresponding tumor xenografts. (D). Expression of RPS6KB1 protein was increased in both PCa cell lines and the corresponding tumor xenografts following the knockdown of miR-195. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was measured as internal control. The semi-quantification of RPS6KB1 protein was measured relative to GAPDH. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with control. Data were presented as Mean ± SD.