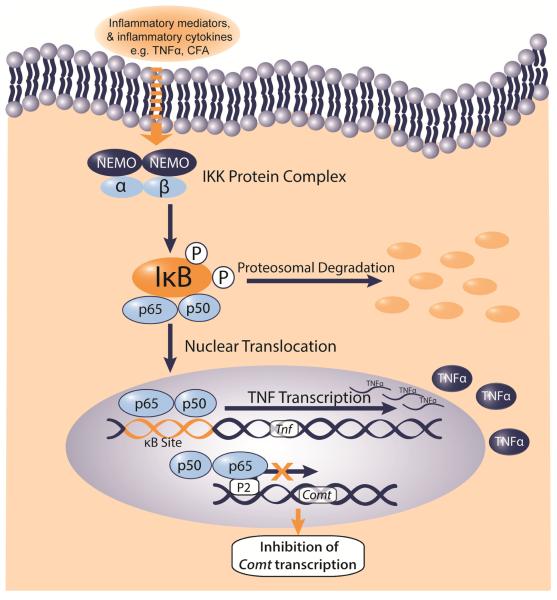
Figure 5.
Schematic depicting how NF-κB mediated transcription of TNFα may regulate COMT expression. Our in vivo data, together with in vitro findings from Tchivileva et al., 2009, suggest an NF-κB-dependent mechanism in which a pro-inflammatory stimulus such as TNFα or CFA can initiate NF-κB, thereby permitting nuclear translocation of p65, which subsequently binds to the P2 promoter of COMT and prevents its transcription.