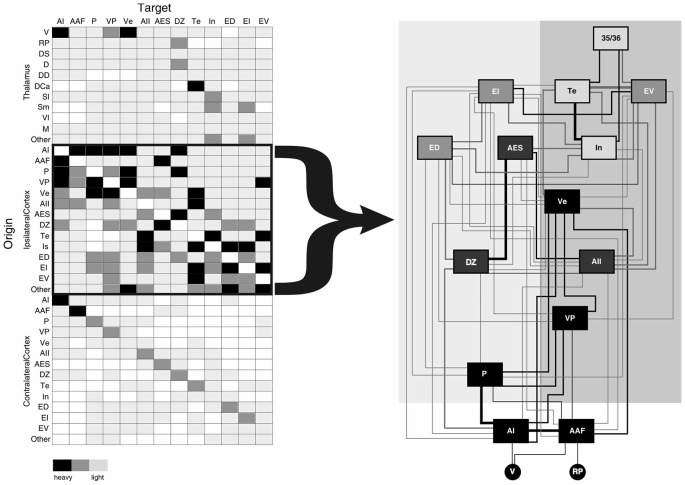
Figure 1.
Schematic summary of convergent projections from thalamic and cortical sources to the thirteen areas of the cat auditory cortex (AI). Left panel depicts a simplified schematic of the relative input arising from each thalamic and cortical source based on the percent input to each area. Right panel depicts a serial hierarchical ordering of auditory cortical areas in the cat based on the laminar origins of cortical projections. Such a cortical hierarchy (right panel) reflects the notion that the numerous corticocortical projections (left panel) are the main determinants of information processing in higher cortical areas. Neglected in this view are roles for the several non-primary thalamocortical (as well as the commissural cortical) inputs to each auditory area, which also contribute fewer, yet potentially salient convergent information to each area. Shading intensity on left panel depicts relative strength of inputs (heavy, medium, weak). Area box shading in right panel indicates type of auditory area (black = tonotopic, dark gray = non-tonotopic, medium gray = polymodal association, light gray = limbic) and line weights reflect average connectional strength indicated in left panel. Figure adapted from Lee and Winer (2011a). Abbreviations: AAF, anterior auditory field; AES, anterior ectolsylvian sulcal area; AI, primary auditory area; AII, second auditory cortex; D, dorsal division of the medial geniculate body (MGB); DCa, dorsal caudal nucleus of the MGB; DD, deep dorsal nucleus of the MGB; DS, dorsal superficial division of the MGB; DZ, dorsal auditory zone; ED, dorsal posterior ectosylvian area; EI, intermediate posterior ectosylvian area; EV, ventral posterior ectosylvian area; In, insular cortical area; M, medial division of the MGB; MGB, medial geniculate body; P, posterior auditory area; RP, rostral pole of the MGB; Sl, lateral suprageniculate nucleus; Sm, medial suprageniculate nucleus; Te, temporal auditory area; V, ventral division of the MGB; Ve, ventral auditory area; Vl, vetrolateral nucleus of the MGB; VP, ventroposterior auditory area.