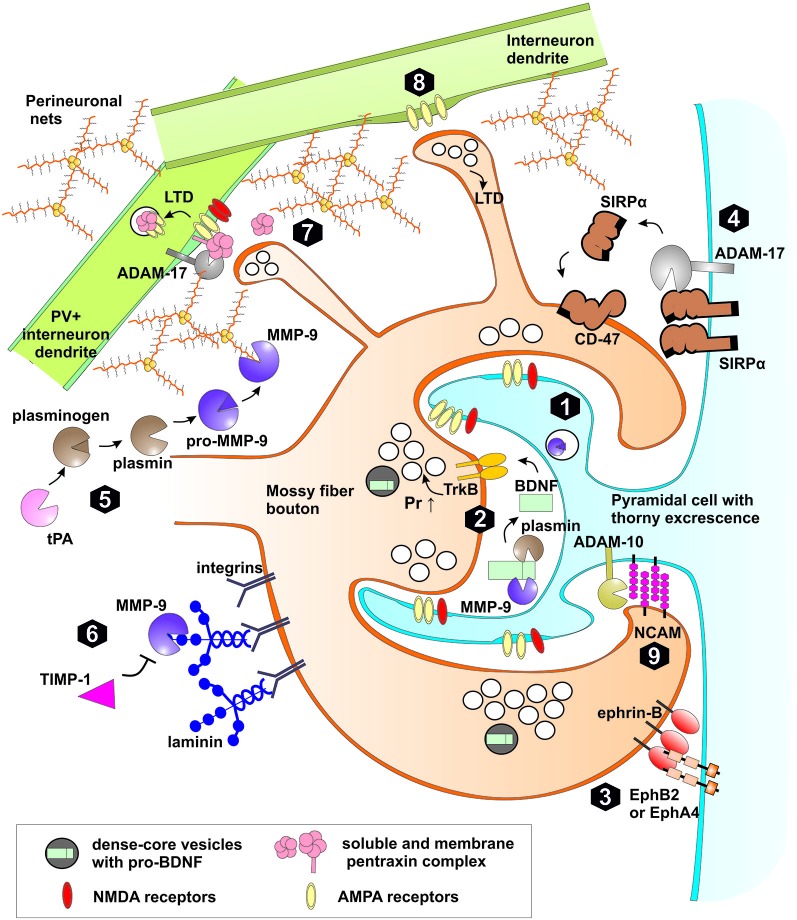
Figure 3.
Extracellular proteolysis in plasticity of mossy fiber synapses. (1) High frequency stimulation leads to synthesis, release of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) to extracellular space and LTP induction in MF-CA3 synapse through increased probability of neurotransmitter release (Pr ↑). (2) MMP-9 or plasmin both activated by tPA cleaves pro-BDNF to mature form. BDNF activates TrkB receptor in the pre and postsynaptic membranes. TrkB activation affects the machinery of neurotransmitter release. (3) Trans-synaptic Eph receptor-ephrin B signaling is crucial for induction of hippocampal mossy fiber LTP. MMPs as well as neuropsin may cleave postsynaptic EphB receptors or presynaptic ephrin ligands. (4) Activity-dependent cleavage by MMPs and ADAM-17 of postsynaptic Signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) followed by shedding of the ectodomain. The released extracellular domain of SIRPα binds to presynaptic CD47 receptor and promotes the maturation of the presynaptic terminals and LTP. (5) Activation of pro-MMP-9 in stratum lucidum requires proteolytic processing of the propeptide domain. Plasmin activated by tPA is a possible proteolytic activator of MMP-9. After activation MMP-9 and other MMPs (e.g., MMP-3) may cleave proteins of perineuronal nets (PNNs) that enwrap PV+ interneurons and restrict synaptic plasticity. (6) MMP-9 regulates mossy fiber synaptic physiology through integrin receptors by cleavage of extracellular matrix (ECM) components (e.g., laminin), release of latent integrin ligands and activation of integrin-dependent signaling pathways. Binding of endogenous inhibitor TIMP-1, secreted in neuronal activity-dependent manner terminates the activity of MMP-9 in the extracellular space. (7) Pentraxin complex composed of membrane pentraxin receptor Npr and two soluble proteins NPTX1 and NPTX2 binds and clusters synaptic AMPA receptors in excitatory synapses on interneurons. During induction of LTD, ADAM-17 cleaves Npr releasing pentraxin complex leading to AMPARs internalization. (8) In a subset of MF-INT synapses containing calcium permeable AMPA receptors and lacking NMDA receptors, presynaptic LTD can be developed in response to MF high frequency stimulation. (9) Synaptic ADAM-10 cleaves NCAM adhesion protein affecting the morphology of MFB.