Table 4.
In silico study results.
| Ligand name/PubChem ID | Substrate | Target molecule (PDB ID) |
k
i
EI complex (µM) |
E
binding of EI complex (kcal/mol) |
Docking score (3) |
Predicted inhibition mode | Inhibition mode in the previous study | Reference | H-bond interaction | Graphical image of ligand-molecule complex |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betulin/CID 72326 | Maltose | Rattus alpha amylase model | 13.66 | −6.66 | 23.36 µM 23.36 µM ≈ 29.99 µM |
Noncompetitive | — | — | ASN374, ASN374, ASN376 |
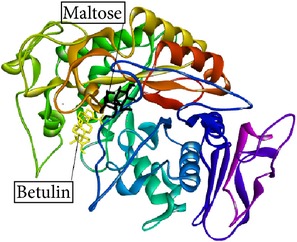
|
|
| ||||||||||
| Betulinic acid/CID 64971 | Maltose | Porcine pancreatic α-amylase (1.ose) | 75.66 | −5.62 | 149.13 µM 149.13 µM ≈ 144.26 µM |
Noncompetitive | Non competitive |
Karthic et al. [14] | — |
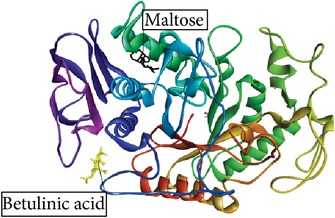
|
|
| ||||||||||
| Bisdemethoxycurcumin/ CID 5315472 |
Maltose | Human alpha amylase (3.old) | 45.86 | −5.92 | 83.49 µM 83.49 µM ≠ 39.55 µM |
Un competitive or competitive |
Un competitive |
Najafian [15] | ARG389 |
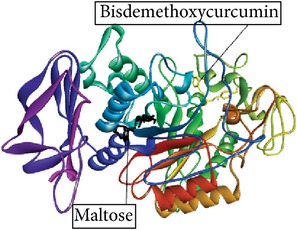
|
|
| ||||||||||
| Curcumin/CID 969516 | Maltose | Human alpha amylase (3.old) | 260.62 | −4.89 | 841.04 µM 841.04 µM ≠ 0.044 µM |
Un competitive or competitive |
Competitive | Karthic et al. [14] | LYS 200, GLY 306, HIS 201 |
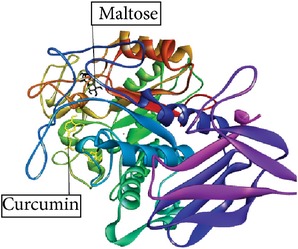
|
Graphical image showed interaction between ligand-substrate and enzyme complexes. Yellow color is ligand, black color is substrate, and whole structure is of amylase.
