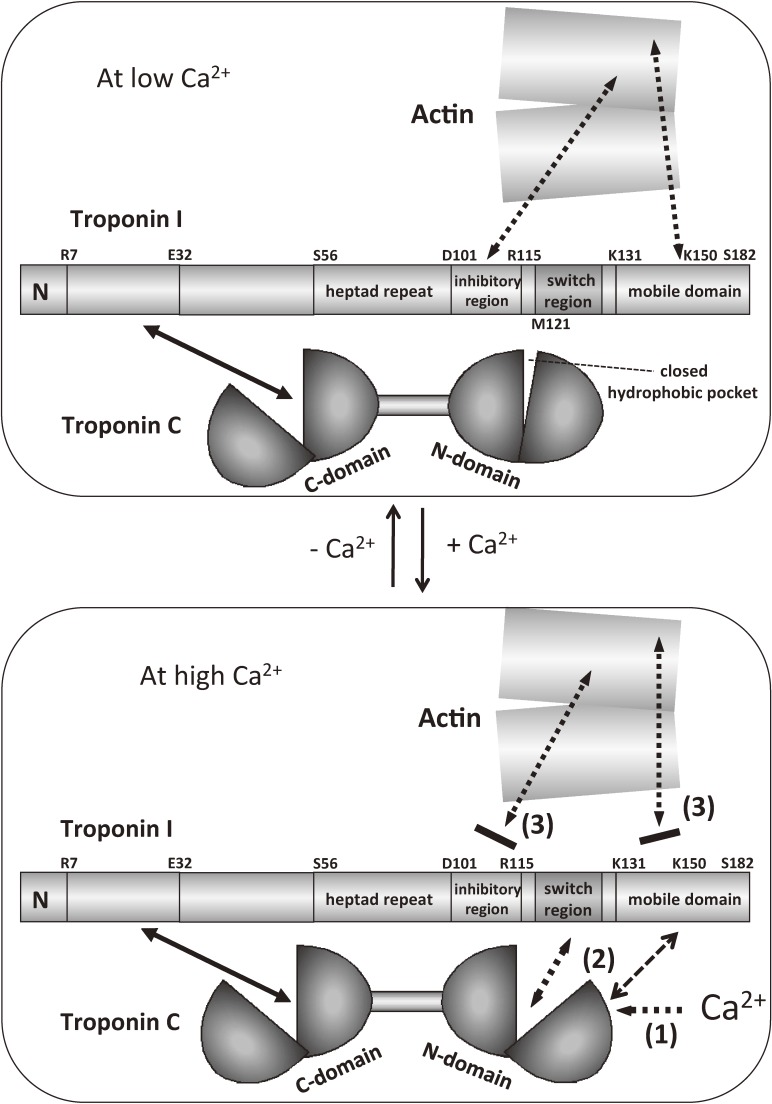
Figure 10.
Schematic model of the Ca2+-induced changes in the mode of interaction between actin and troponin.105) Step 1: Ca2+ binds to the N-domain of TnC, and the hydrophobic pocket opened. Step 2: the association between the switch region of TnI and the N-domain of TnC becomes tighter. Step 3: the inhibitory region and the mobile domain of TnI detach from actin, and this detachment is a key step to trigger the activation of muscle contraction. Note that actin is not just a target of Ca2+-regulation, but is an important component of the Ca2+-switch. The mobile domain of TnI shuttles between actin (at low Ca2+ concentrations) and the main body of troponin (at high Ca2+ concentrations). Solid arrows indicate permanent interactions, whereas the dotted arrows indicate regulated interactions.