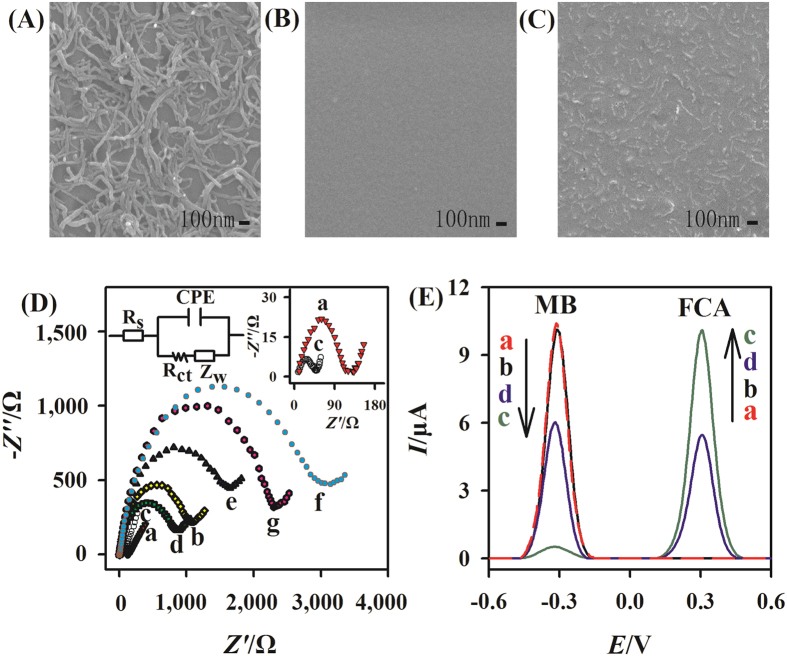
Figure 2. Characterization and Feasibility of the developed aptasensor for prion assay.
SEM images: (A) MWCNTs, (B) β-CD, (C) MWCNTs-β-CD composites. (D) Electrochemical impedance spectra (Nyquist plots) of the different modified electrodes in 0.1 M KCl aqueous solution containing 5 mM (1:1) [Fe(CN)6]3–/4–. (a) Bare GC electrode, (b) β-CD/GC electrode, (c) MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode, (d) MB-Apt/MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode, (e) BSA/MB-Apt/MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode, (f) prion/BSA/MB-Apt/MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode, and (g) FCA/prion/BSA/MB-Apt/MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode. Inset: equivalent circuit model for electrochemical impedance measurement system (the upper left corner) and the nyquist plots of the bare GC electrode and MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode (the upper right corner). (E) SWV curves of the different electrodes. (a) BSA/MB-Apt/MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode, (b) BSA/MB-Apt/MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode incubated with 200 nM prion, (c) BSA/MB-Apt/MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode incubated with 20 μM FCA without prion, (d) BSA/MB-Apt/MWCNTs-β-CD/GC electrode incubated with 1 pM prion and then 20 μM FCA.