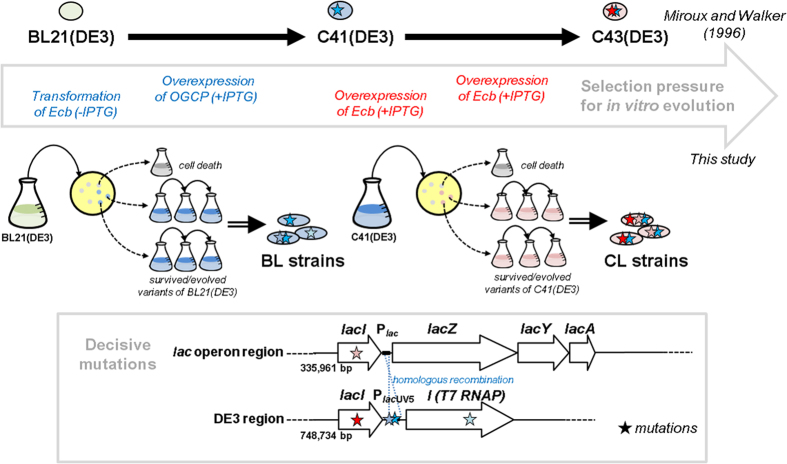
Figure 5. Overview of the in vitro evolution of E. coli strains overexpressing membrane proteins.
A scheme to generate BL and CL strains that are capable of overcoming the toxicity from transformation with or overexpression of Ecb, respectively, are shown in the upper part of the figure. The selection of C41(DE3) from BL21(DE3), and C43(DE3) from C41(DE3), was conducted previously12. The mutational hotspots in the evolved strains and the probable mechanisms producing them are illustrated at the bottom. Mutational hotspots were located in the lacUV5 promoter of the DE3 region and in the lacI gene of the lac operon, which were identified as decisive mutations that made E. coli cells tolerant to the overexpression of membrane proteins (Wagner et al.11 and this study). The mutations in the lacUV5 promoter in the DE3 region result from homologous recombination with the similar lac promoter in the lac operon.