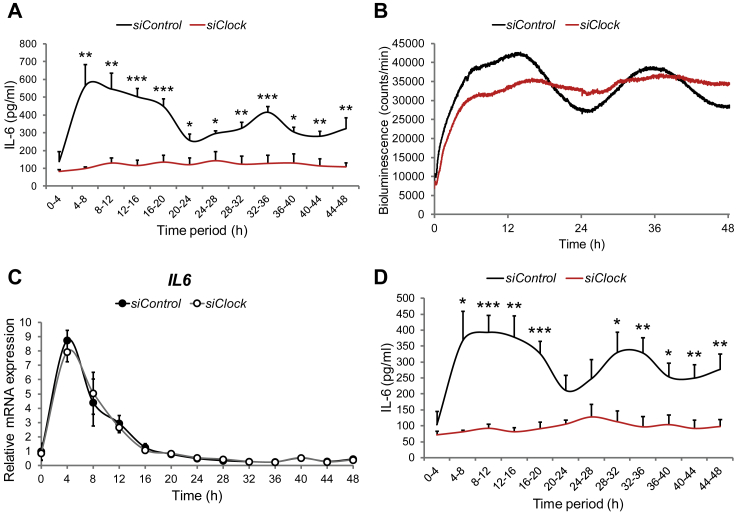
Figure 3.
Basal IL-6 secretion by human skeletal myotubes is strongly inhibited in the absence of a functional circadian clock. Myoblasts were transduced with the Bmal1-luc lentivector, differentiated into myotubes and transfected with either siControl or siClock siRNA. 24 h following transfection, myotubes were synchronized with forskolin and subjected to continuous perifusion with parallel bioluminescence recording. (A) Basal IL-6 secretion profile (mean + SEM) in the presence or absence of a functional clock. The perifusion outflow medium was collected continuously in an automated manner in 4 h intervals until 48 h (0–4 corresponds to the accumulation of IL-6 between 0 h and 4 h). IL-6 levels in the perifusion outflow medium were assessed by ELISA. The results represent basal IL-6 levels normalized to the total DNA content. 2 technical duplicates from 3 independent experiments (3 non-obese donors, see Table 3) were analyzed for each time point. (B) Bmal1-luc bioluminescence profiles of siControl-transfected myotubes (black line) and siClock-transfected myotubes (red line), representative of 3 experiments, with one donor cell line used per experiment. (C) RT-qPCR was performed for IL6 on RNA samples extracted from forskolin-synchronized human myotubes, transfected with siClock (open circles) or siControl (closed circles). Samples were collected every 4 h and normalized to the mean of 9S/HPRT. Profiles (mean ± SEM) are representative of 3 experiments (2 donors for time points 0 h–48 h and 3 donors for time points 12 h–36 h) with duplicates per time point. (D) Basal IL-6 secretion profiles in the presence or absence of a functional clock obtained from concentrated perifusion samples, assessed by multiplex analysis. Data shown as mean + SEM of 2 technical duplicates from 3 biological samples for each time point, normalized to the total DNA content.