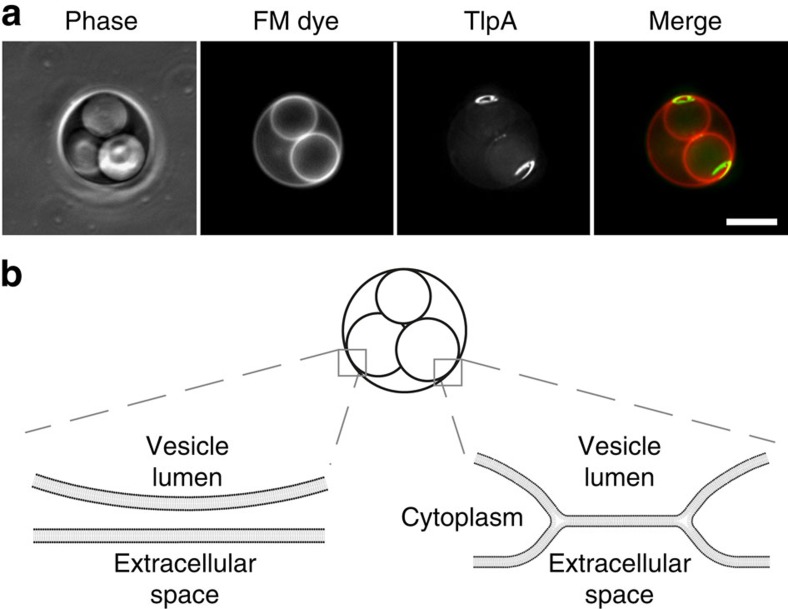
Figure 4. TlpA is recruited to non-septal curved membranes.
(a) The differential staining of internal vacuole-like structures with membrane dye FM 4–64 in B. subtilis L-forms indicates the presence of two distinct types of vacuoles within the cell32. The membrane dye FM 4–64 is not able to cross biological membranes and therefore does not stain internal membrane structures, unless they remain connected to the cytoplasmic membrane62,63. The connection with the cytoplasmic membrane (membrane hemifusion) generates membrane areas with a distinct curvature. TlpA-GFP is strongly recruited to these non-septal areas of high membrane curvature. Maximal intensity projection of a deconvolved optical sectioning is shown. Strain used: B. subtilis HS55 (Pxyl-tlpA-gfp L-form). Scale bar, 5 μm. (b) Schematic depiction of the interfaces between the vacuolar and cytoplasmic membranes. In the left, the membranes are fully separated resulting in a lack of FM 4–64 staining. In the right, the membranes remain attached via membrane hemifusion, allowing lateral diffusion of FM 4–64.