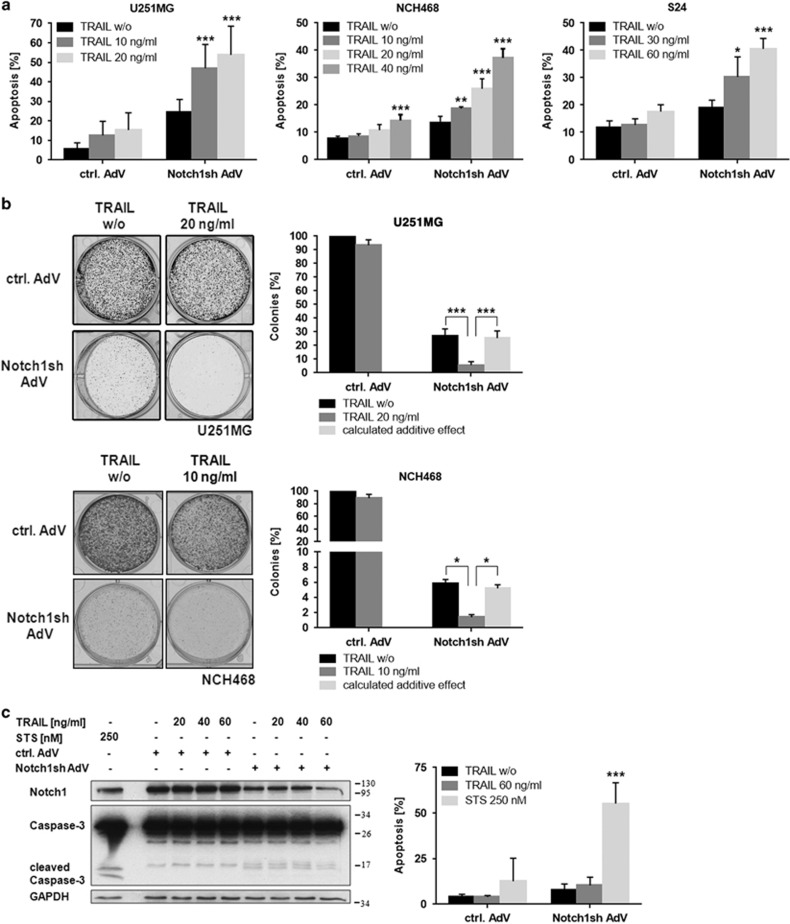
Figure 1.
Notch1 inhibition sensitizes glioblastoma cells for TRAIL treatment. (a) Glioblastoma cells (U251MG-long-term cell line; NCH468-primary culture; S24-glioblastoma initiating cells) transduced with control-AdV or Notch1sh-AdV (72 h) were treated with TRAIL for 24 h (increased TRAIL concentrations were used for S24 cells because of the high TRAIL resistance of cancer-initiating cells). Apoptotic cell death was measured by flow cytometry (n=3; mean ±S.D.). P-values were determined by two-way ANOVA. (b) Notch1 inhibition together with TRAIL treatment strongly reduces colony formation of glioblastoma cells. Control-AdV and Notch1sh-AdV transduced U251MG and NCH468 cells were seeded in 6-well plates 24 h post transduction (U251MG: 1 × 104 cells; NCH468: 4 × 104 cells). Cells were treated with TRAIL 48 h following seeding and 72 h post transduction, respectively. Colony growth was assessed by crystal violet staining 6 days (U251MG) or 5 days (NCH468) after seeding. Representative staining results are shown (left panels). Colony growth was quantified from three independent assays (right panels). P-values were determined by one-way ANOVA test. (c) Notch1 inhibition followed by TRAIL treatment does not target astrocytes. Human astrocytes transduced with control-AdV or Notch1sh-AdV (72 h) were treated with varying concentrations of TRAIL or 250 nM STS for 24 h. Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis for Notch1 and Caspase-3 (left panel) or apoptotic cell death was measured by flow cytometry (n=3; mean±S.D.) (right panel). P-values were determined by two-way ANOVA. STS treated astrocytes served as a positive control for Caspase-3 cleavage and apoptosis, respectively