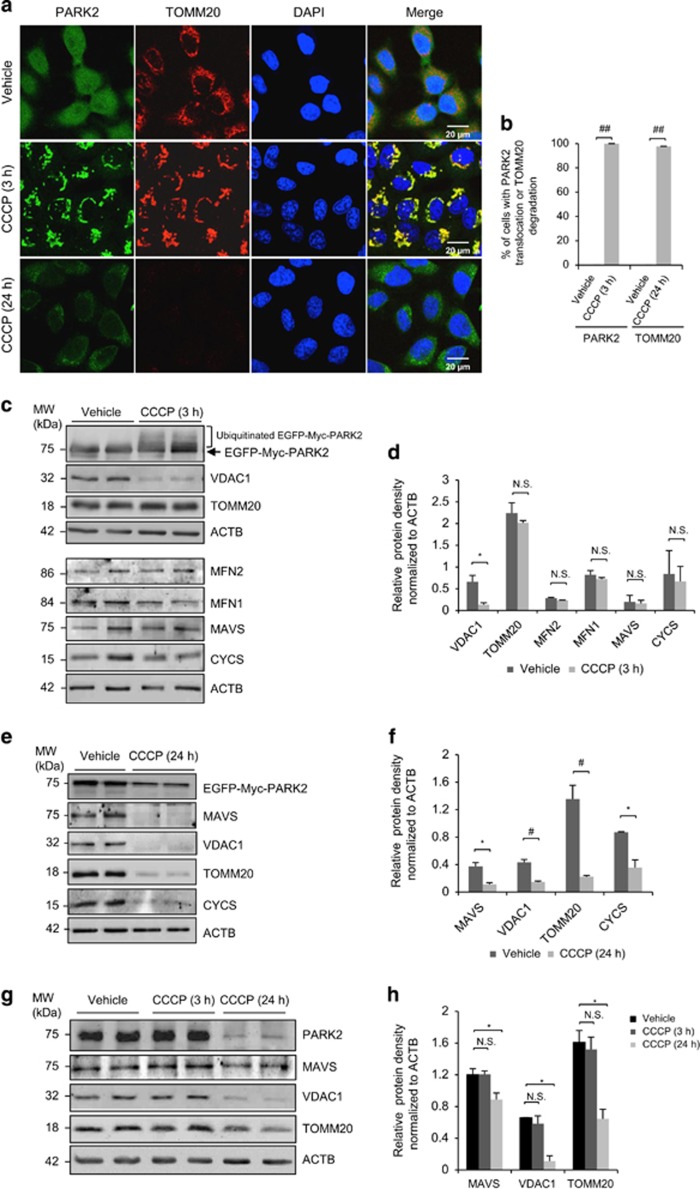
Figure 1.
CCCP treatment induces perinuclear aggregation and degradation of mitochondrial proteins in HeLa cells stably expressing PARK2. (a, c, and e) HeLa cells stably expressing EGFP-Myc-PARK2 were treated with either vehicle or CCCP (10 μM) for 3 or 24 h as indicated. PARK2 signal was shown in green. Cells were immunostained for TOMM20 (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Western blotting was performed to examine the levels of various mitochondrial proteins as indicated at 3 h (c) and 24 h (e) post CCCP treatment. ACTB/β-actin was probed as a loading control. (b) The percentage of cells with PARK2 translocation to mitochondria (left) or TOMM20 degradation (right) relative to total number of cells in (a) is presented. Quantification was performed based on three images with each image containing at least 30 cells (mean±standard deviation (S.D.), n=3). ##P<0.001. (d and f) Densitometric analysis of protein levels after normalized to ACTB in (c) and (e) (mean±S.D., n=3), respectively. *P<0.05; #P<0.01; NS, not significant. (g) SH-SY5Y cells, a human neuroblastoma cell line with relatively high expression of endogenous PARK2, were treated with vehicle or CCCP (10 μM) for 3 or 24 h as indicated. Western blotting was carried out to examine the protein levels of PARK2, VDAC1, TOMM20, and MAVS. ACTB/β-actin was probed as a loading control. (h) Densitometric analysis of protein levels of VDAC1, TOMM20, and MAVS after normalized to ACTB (mean±S.D., n=3). *P<0.05; NS, not significant