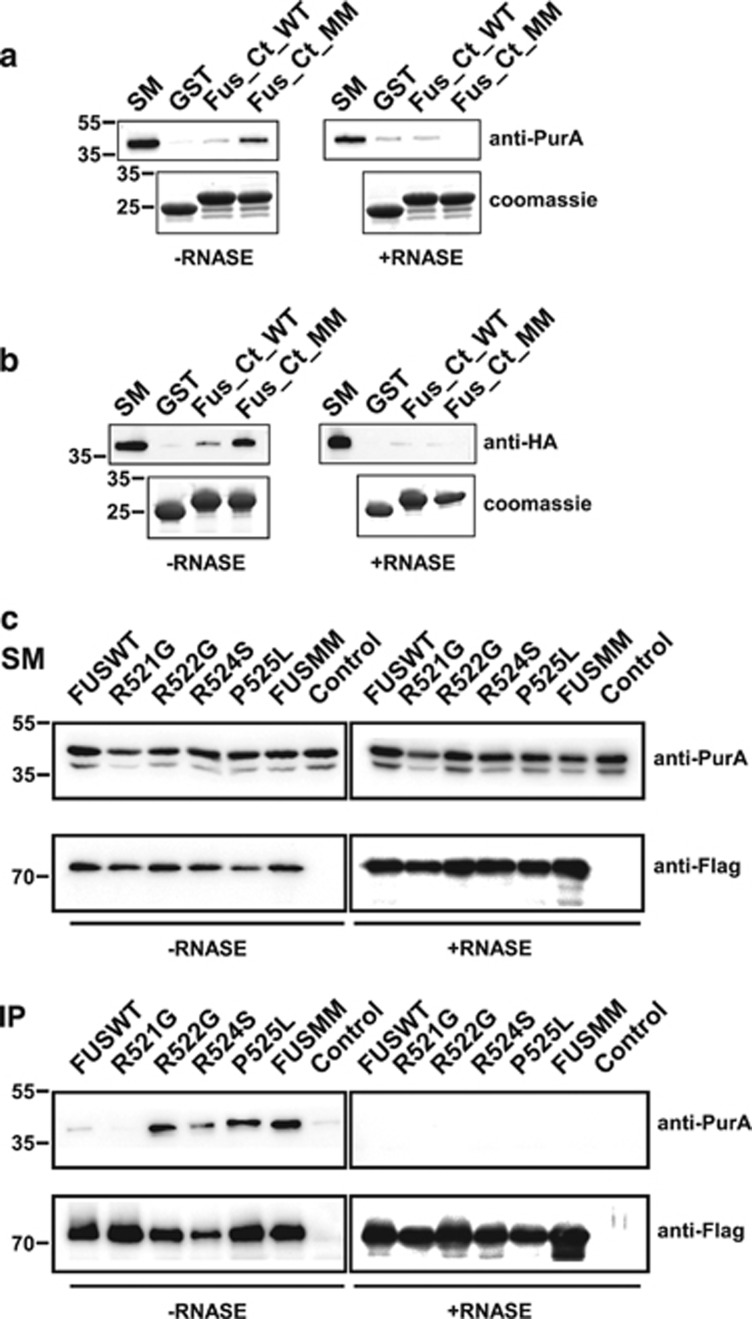
Figure 1.
FUS/Pur-alpha physical interaction. (a) GST, GST-fused C-terminal region of wild-type FUS (FUS_Ct_WT), and GST C-terminal domain of multimutated FUS (FUS_Ct_MM) were used as baits in affinity purification experiments from a rat brain Triton X-100 extract, in the presence or absence of RNAse. Affinity-purified material retained by the GST fusion proteins was resolved by SDS-PAGE and processed by western blotting with anti-Pur-alpha antibody (top). The same volume of eluted material analyzed by western blotting was separated on a different SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue to verify equal loading of the different GST fusion baits (bottom). 1 : 500 of total brain extract and 1:50 of proteins retained from each column were loaded on the gel. SM, starting material. (b) Interaction between the same GST fusion proteins utilized in (a) and in vitro-translated HA-tagged Pur-alpha was tested by pull-down in the presence or absence of RNAse. HA Pur-alpha bound to the GST fusion proteins was resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting with anti-HA antibody. GST fusion proteins used in the pull-down assay were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue (bottom). 1 : 50 of reticulocyte extract exploited in the pull down and 1:3 of proteins retained from each column were loaded on the gel. (c) Protein extracts from HeLa cells expressing HA-Pur-alpha on its own (Control), or together with FUSWT, FUS carrying single mutations (R521G, R522G, R524S, or P525L), or FUSMM were incubated with or without RNAse and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody. Retained proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting with anti-HA and anti-Flag antibodies. 1 : 50 of total cell extract utilized for each immunoprecipitation and 1 : 3 of bound proteins were loaded on the gel. SM, starting material; IP, immunoprecipitate