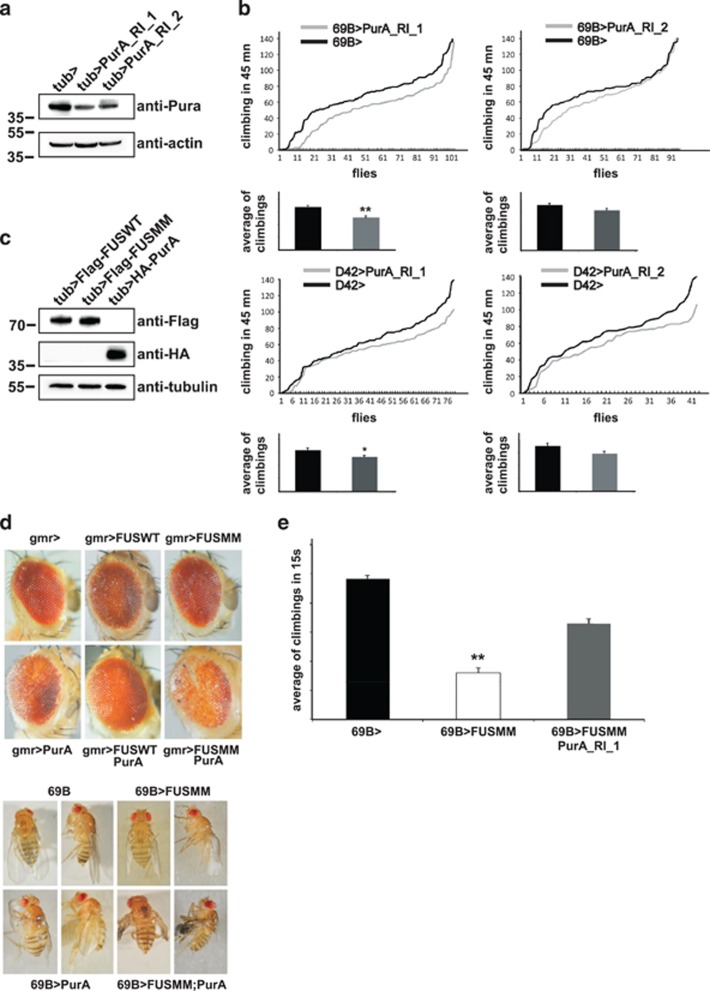
Figure 7.
In vivo role of Pur-alpha in Drosophila melanogaster. (a) RNAi mediated downregulation of Pur-alpha in all Drosophila tissues by the expression of Pur_alpha_RNAi_1 and Pur_alpha_RNAi_2 RNAi under control of the ubiquitous driver tubulin-GAL4. Total extracts from RNAi expressing flies and control animals were separated by SDS-PAGE and the extent of Pur-alpha downregulation was evaluated by western blotting with an anti-Pur-alpha antibody. (b) The same RNAi fly lines of (a) were crossed at 29 °C with the pan neuronal driver 69B (upper panels) and with the motoneuron driver D42 (lower panels). Climbing performance of each offspring is represented by plotting the total number of climbing events for each fly of the group. Numbers of climbing events for all flies of the group were ascending ordered and plotted. Statistical significance was evaluated with Student's t-test (** high statistical significance, P-value <0.001; * statistical significance, P-value <0.05) and the averages of climbing events in each population, with corresponding standard errors, are shown. (c) Expression level of FUSWT, FUSMM, and Pur-alpha mammalian proteins in fly eyes. Heads from flies expressing the transgenes under GMR were separated and homogenized. Protein extracts were separated on SDS-PAGE and the expression of each transgene was evaluated by western blotting. (d) Genetic interaction of FUSMM and Pur-alpha in Drosophila eye. Eyes of flies expressing the mammalian genes under control of GMR Gal4 are shown. FUSWT and Pur-alpha induces respectively very mild and mild eye degeneration, while expressing FUSMM does not determine any visible phenotype. A simultaneous expression of both FUSMM and Pur-alpha causes strong eye degeneration. Pictures of flies expressing the transgenes under the pan neuronal driver 69B are shown. FUSWT expression causes early fly lethality (not shown), while FUSMM induces an alteration of wing extension; similar unextended wings are observed in flies expressing Pur-alpha. Expression of both FUSMM and Pur-alpha generates a more severe alteration of wing morphology. (e) Fly lines expressing FUSMM on its own, or combined with Pur_alpha_RNAi_1, were crossed with 69B-GAL4 pan neuronal driver, at 25 °C. A negative geotaxis assay was performed to measure climbing activity of flies with different genotypes. Averages of climbing evens are shown together with corresponding standard errors. Downregulation of Pur-alpha in neurons expressing FUSMM significatively improves fly climbing activity. Statistical significance was evaluated with Student's t-test (values significantly different from relative controls are indicated with two asterisk; P<0.001)