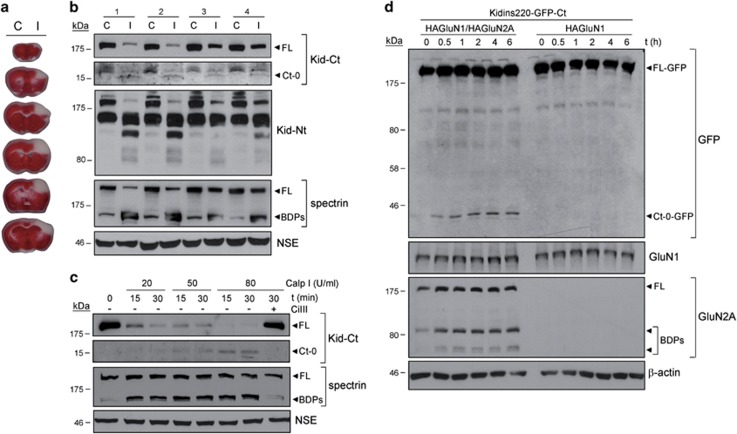
Figure 2.
Kidins220 sequences approximately 15 kDa from the C-terminus are major calpain targets after calpain activation in vivo and in vitro. (a) Brain coronal sections of mice subjected to transient cerebral ischemia induced by dMCAO incubated with vital stain TTC showing a cortical infarct in the MCA territory of the ipsilateral hemisphere. MCA was compressed for 1 h followed by blood reperfusion for 24 h. (b) Analysis of Kidins220 processing after in vivo excitotoxicity induced by transient cerebral ischemia. Protein extracts were prepared from cortical infarcted regions (I) and corresponding areas of the contralateral hemisphere (C) of four mice subjected to dMCAO (1–4). Immnuoblot analysis of Kidins220 processing established a correlation between the degree of calpain activation, demonstrated by spectrin cleavage, the decrease of FL Kidins220, and the accumulation of different N-terminal intermediates (Nt-s) and a 15-kDa C-terminal fragment (Ct-0). The presence of this Ct-0 fragment, observed in longer exposures of Kid-Ct immunoblots, was higher in animals presenting a better calpain activation. (c) Protein extracts from cortical neurons subjected to in vitro digestion with purified calpain I (0, 20, 50 or 80 U/ml) for 15 or 30 min in the absence or presence of calpain inhibitor CiIII (20 μM). The decrease of FL Kidins220 due to calpain activity correlated with the generation and accumulation of a major 15 kDa C-terminal fragment (Ct-0). (d) Analysis of Kidins220 C-terminal fragments produced in a heterologous system of excitotoxicity. To facilitate detection of C-terminal fragments, Kidins220 rat-coding sequence fused to GFP at its C-terminus (Kidins220-GFP-Ct) was expressed in HEK293T cells together with HA-tagged GluN1 and GluN2A, to produce a functional NMDAR, or GluN1 only, yielding an incomplete NMDAR. In HAGluN1/HAGluN2A-transfected cells stimulated with NMDA (0–6 h), GFP antibodies mainly detected FL Kidins220-GFP-Ct (FL-GFP) and its fragment Ct-0-GFP. In parallel, and in contrast to GluN1, subunit GluN2A (FL) was also processed and produced BDPs as expected for a calpain substrate. Neuronal-specific enolase (NSE) or β-actin levels were used as protein-loading controls