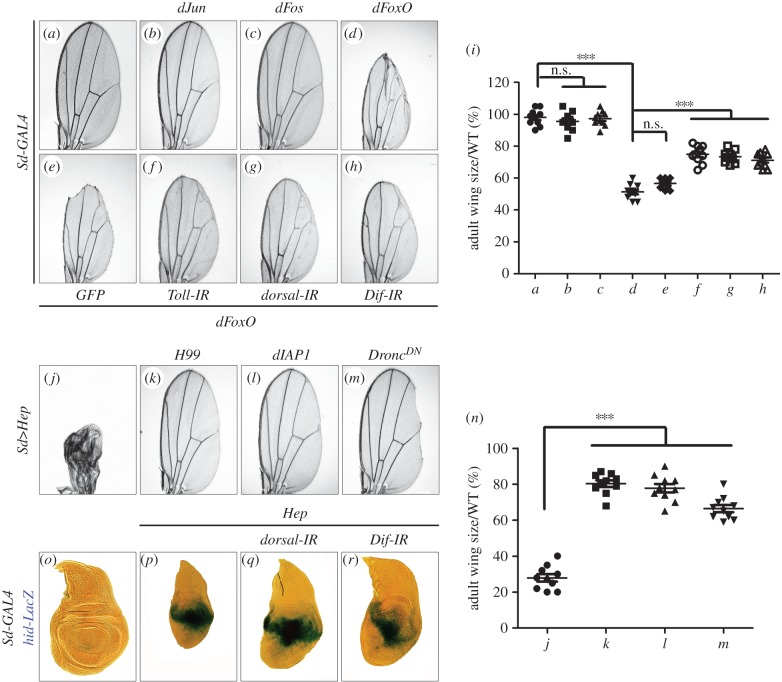
Figure 5.
Toll signalling acts downstream of FoxO and mediates caspases-independent cell death. (a–h and j–m) Light micrographs of Drosophila adult wings are shown. Compared with Sd-GAL4 control (a), ectopic expression of dFoxO results in an evident reduction in wing size (d), which is suppressed significantly by loss of Toll signalling (f–h), but not that of GFP (e). Expression of dJun or dFos driven by Sd-GAL4 does not produce any visible defects (b and c). The small wing phenotype induced by Sd>Hep (j) is strongly suppressed by Df(3L)H99 that deletes one copy of the apoptotic genes reaper, hid and grim (k), the expression of DIAP1 (l) or DroncDN (m). (i and n) Quantifications of adult wing size/wild-type (WT) ratio shown in figures a–h and j–m, respectively (n = 10). One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute p-values, significance was indicated with asterisks (***p < 0.001); n.s., not significant. (o–r) X-Gal staining of a hid-LacZ reporter in wing discs. Compared with the control (o), expression of Hep in the wing pouch driven by Sd-GAL4 induces hid transcription (p), which cannot be suppressed by knocking-down dorsal or Dif (q and r). See the electronic supplementary material for detailed genotypes.