Figure 4.
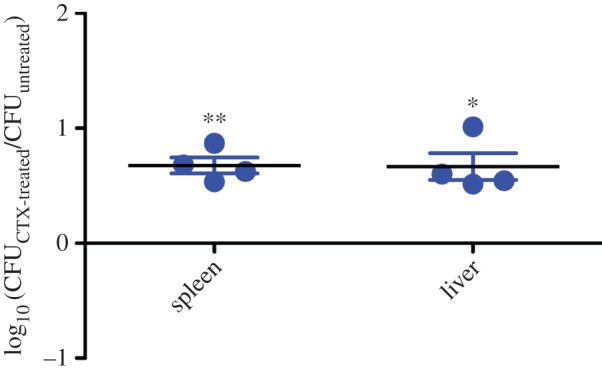
Increased systemic colonization of S. Typhimurium exposed to a sub-inhibitory concentration of CTX during anaerobic growth. Groups of five BALB/c mice were inoculated IP with a 1 : 1 mixture of the ΔphoN::Kan mutant grown in the presence of CTX (0.065 mg l−1; 0.5× MIC) and the ΔphoN::Cam mutant grown in the absence of the antibiotic. After 2 days of infection, mice were euthanized and the liver and spleen were aseptically removed and homogenized in sterile PBS. Bacterial load recovered from each organ was determined by plating serial 10-fold dilutions on LB agar plates with the appropriate antibiotics. CI values were calculated as a mean ratio of CTX-treated to untreated control, normalized to the input ratio and converted logarithmically. Error bars denote standard error. Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student's t-test. Asterisks indicate normalized output ratios that were significantly statistically different from zero, the ideal value obtained when both strains colonize to the same extent (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
