Figure 8.
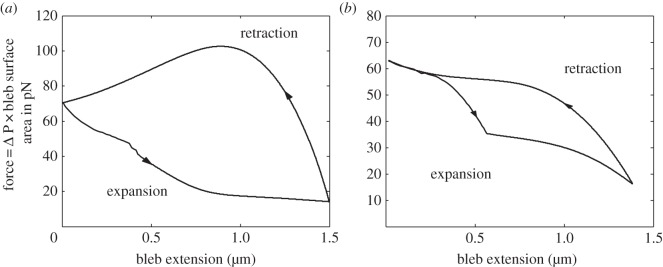
Force–extension curves for the expansion and retraction of blebs from different initiation mechanisms. (a) Bleb created through global cortex contraction. (b) Bleb created through localized membrane growth. In both cases, as a bleb expands, the cellular pressure (and, hence, force acting on the bleb) drops because of the assumption of constant solution volume. Conversely, as the bleb retracts the pressure increases. Note that hysteresis is present in the force–extension blebbing cycle. Parameters are the same as in figure 6.
