Fig. 1.
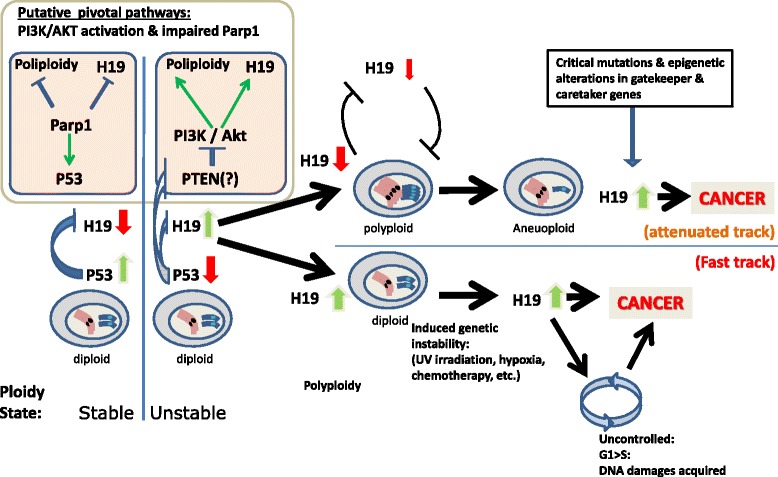
H19 in genomic instability. Cells maintain their normal ploidy state depending on normal expression of P53, possibly in a Parp-1 dependent manner. Reduction of P53 level (when Parp-1 is impaired?), leads either to polyploidy (attenuated track that prevents cancer progression) or to H19 upregulation (fast track to cancer, lower panel). PTEN > PI3K/Akt may be the basis of both routes. Since polyploidy (upper panel) is a common gateway to chromosomal loss/aneuploidy, which is usually accompanied with deleterious, tumorigenic mutations, it may eventually re-elicit H19 expression with its oncogenic properties
