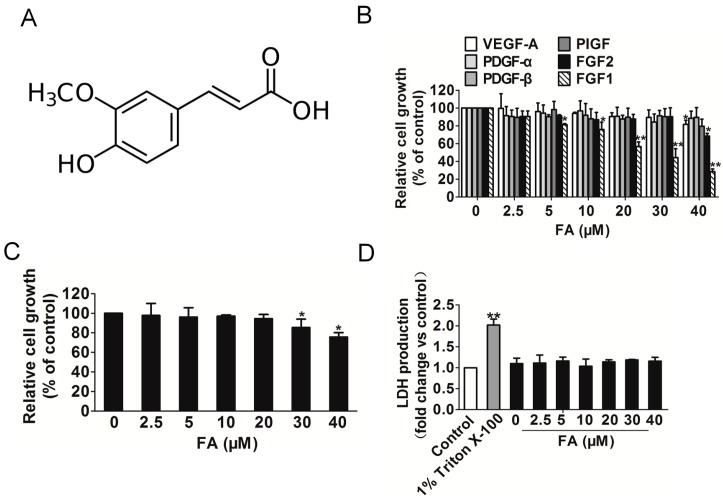
Figure 1.
The effect of FA on HUVEC growth induced by FGF1. (A) The chemical structure of ferulic acid (FA); (B) the proliferation of HUVEC stimulated by FGF1 was significantly decreased by FA in a dose-dependent manner, while FA had little inhibitory effect on HUVEC that were stimulated by other angiogenesis stimulates. Data are from three independent experiments and are the mean ± SD. n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. the control; (C) FA had little inhibitory effect on HUVEC in the absence of FGF1. Data are from three independent experiments and are the mean ± SD. n = 3, * p < 0.05 vs. 0 μM FA treatment; (D) FA administration did not result in LDH release, indicating that FA brought little toxic effect on HUVEC. Data are from three independent experiments and are the mean ± SD. n = 3, ** p < 0.01 vs. the control.