Figure 2.
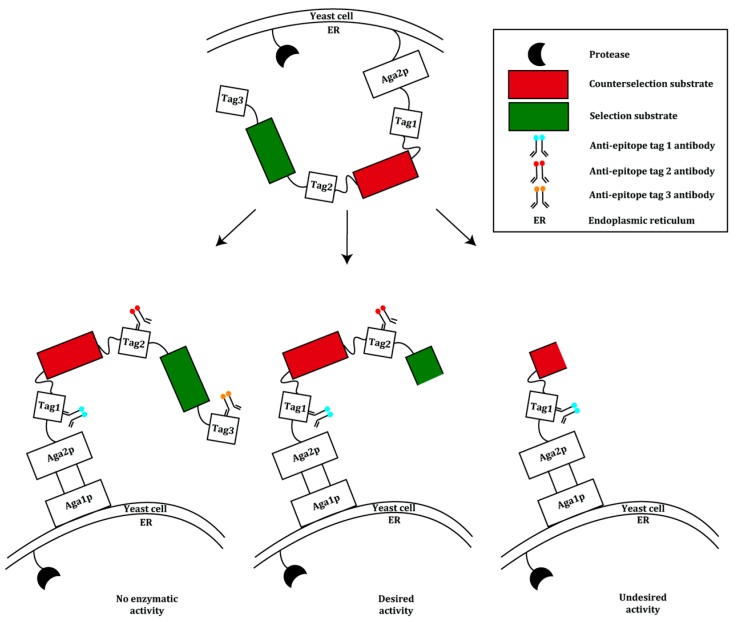
Schematic overview of the yeast endoplasmic reticulum sequestration screening (YESS) system. Both protease and substrate contain a C-terminal endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retention sequence. Within the ER, the protease can move in close proximity to the substrate. Depending on the specificity of the engineered protease, proteolysis of the selection substrate or counterselection sequence takes place. This results in the removal of the ER retention sequence and respective epitope tags located on the substrate fusion polypeptide. The remaining N-terminal portion of the polypeptide is then displayed on the yeast cell surface. Each cell is labeled with fluorescently conjugated anti-epitope tag antibodies and screened using multicolor FACS [24].