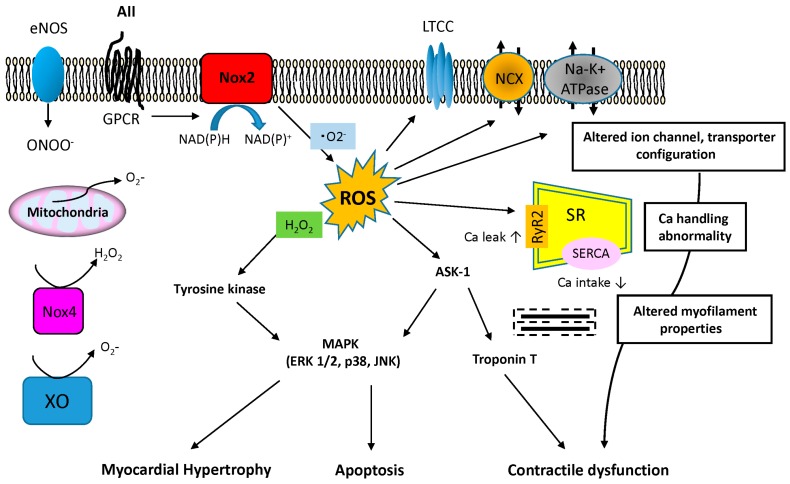
Figure 5.
AII-associated ROS pathway and alternation of the structure and function in cardiomyocyte. AII involves activation of ·O2− production by NADPH oxidase NOX2. AII induces cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis via G-protein-linked pathway that involves ROS-related activation of several downstream signals, including MAPKs (ERK 1/2, p38, JNK). ASK1 is also activated by ROS and in turn activates p38, JNK and induces cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis. ASK1 may promote troponin T phosphorylation and implicate in contractile dysfunction. AII-associated ROS pathway may influence the alternation of structure and function of excitation-contraction coupling and ionic homeostasis, including LTCC, NCX, Na–K+ ATPase and Ca handling. The potential effects of dysregulated ion channel, transporter and calcium in SR are shown. G-protein receptor (GPCR), l type Ca2+ channels (LTCC), Sodium/calcium exchanger (NCX), Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium calcium ATPase (SERCA), Ryanodine receptor (RyR2), Xanthine oxidase (XO).