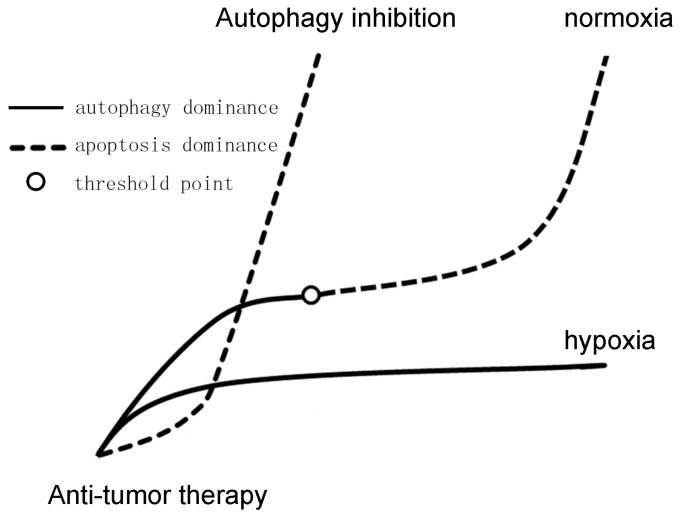
Figure 3.
Autophagy and apoptosis after anti-tumor therapy under hypoxia or autophagy inhibition. Induced autophagy can provide substrates, as well as maintain the functional pool of mitochondria. Stress was solved by autophagic flow, and some apoptosis was activated at first; however, if the saturation point were achieved after prolonged hypoxia, then apoptosis could be dominant. Under hypoxia, autophagy seems to be activated in a more efficient way, leading to magnification of the prosurvival role of autophagy, thereby promoting tumor progression. However, autophagy inhibition may push the cell fate decision from autophagy to apoptosis and exacerbate injury.