Figure 7.
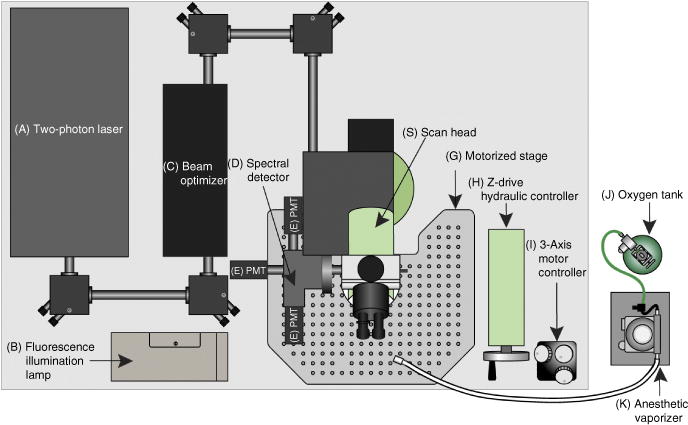
Schematic of the two-photon microscope system used in this protocol. For two-photon imaging, a Ti:sapphire laser generates a beam between 680 and 1,080 nm (A) that is transmitted to the scanner (S) through the beam optimizer (C). Once excitation occurs on the sample, the emission wave is delivered to the spectral detector (D). In the spectral detector, there are two dichroic mirrors (495LP and 560LP) and three filters (450/50, 525/50 and 610/75). Depending on the wavelength, the excitation wave separates into three different PMTs (E). Fluorescence from the sample can be checked visually with wide-field fluorescent illumination (B) before recording. The coordinates of the microscope platform (G) are regulated hydraulically (H) or more precisely with a motorized controller (I). The oxygen tank (J) is connected to the isoflurane vaporizer (K), and the inhalable anesthetic gas is continuously delivered to the mouse through the tubing and a nose cone.
