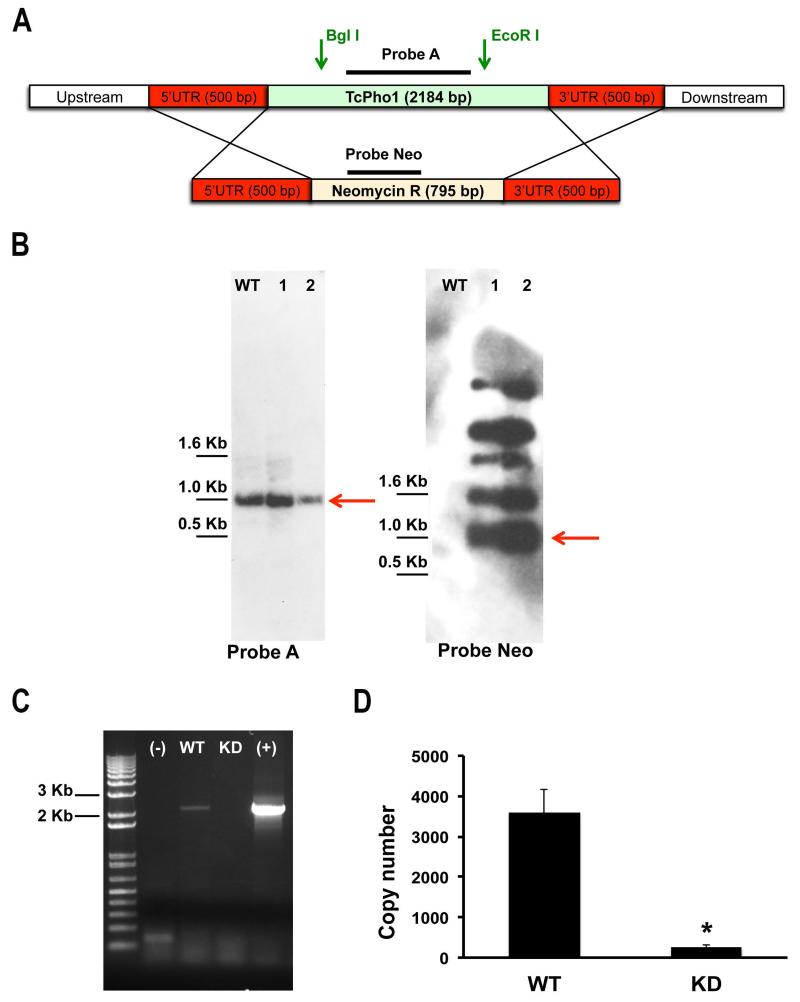
Fig. 4.
Generation of TcPho91 knockdown cell line. A Schematic representation of the strategy used for the generation of a TcPho91 knockout mutant in T. cruzi epimastigotes. One allele of TcPho91 would be replaced with the neomycin-resistance gene by homologous recombination, generating a TcPho91 SKO cell line. B. Southern blot analysis indicates that two neomycin resistant cells lines still conserve the TcPho91 gene (left panel). A probe against the resistant marker showed hybridization signals specific to Neo gene in multiple loci either episomally or integrated into other regions (right panel). C. RT-PCR analysis of wild type (WT) and KD mutants shows considerable decrease in the signal corresponding to TcPho91 mRNA indicating knockdown of TcPho91 expression. Negative (−) and positive (+) controls are also shown. D. Quantification of the results in (C) * p < 0.05.