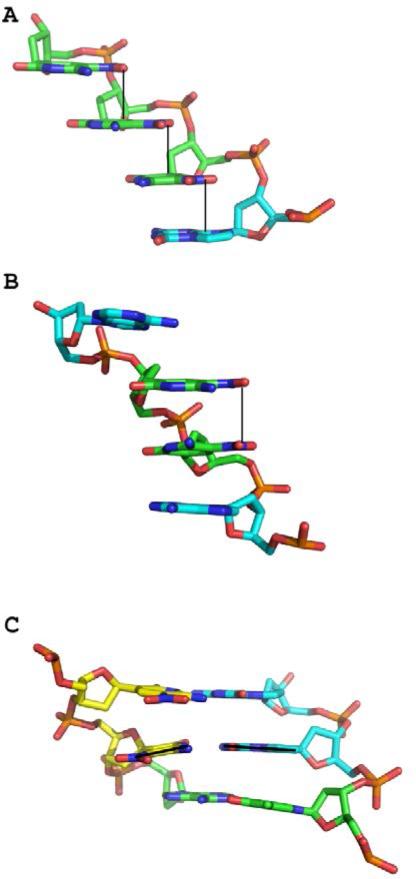
Figure 5.
Structural characteristics of Z:P nucleobase pairs. (A) In A-DNA, the Z-NO2 stack over the pyrimidine or purine ring of the adjacent nucleobase emphasized by solid lines as shown in this stick renderings C, green for Z, cyan for P, O in red, N in blue, and phosphorous in orange for P8Z9Z10Z11, A chain. (B) In B-DNA, the Z-NO2 groups are positioned roughly over one another but do not stack with nucleobase rings. Rather, the pyrimidine rings stack with adjacent nucleobase rings as shown in this stick rendering for bases for A9Z10Z11A12 for the G chain. (C) The central Z:P pair, with a black line indicating the trajectory of each nucleobase, exhibits a large buckle angle as shown in this stick rendering for T5P6P7 (B chain) and Z10Z11A12 (G chain). C atoms are indicated in yellow for Z, cyan for P, and green for A or T, with other atoms as indicated above.