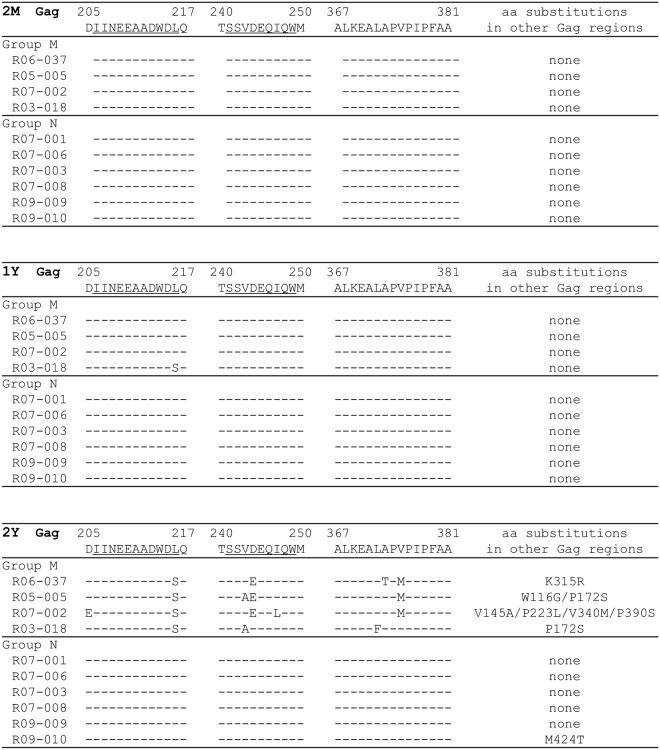
Fig 2. Dominant non-synonymous mutations in proviral gag in SIV controllers.
Amino acid substitutions around SIV Gag206–216, Gag241–249, and Gag367–381 epitopes and in other Gag regions approximately 2 months (2M, top), 1 year (1Y, middle), and 2 years (2Y, bottom) after SIVmac239 challenge are shown. Most of the proviral gag fragments were amplified from CD4+ T cells isolated from PBMCs, while those at 2 years in macaques R06-037, R05-005, R07-001, and R07-006 were from cultured CD4+ T cells due to limitation of available cell numbers. Mutant sequences shown were completely dominant (i.e., wild-type sequences were undetectable at the residues showing mutant sequences) except for the L216S mutation (the ratio of wild type/mutant: 2/5) in macaque R03-018 at 1 year post-infection. No subdominant mutation was detected.