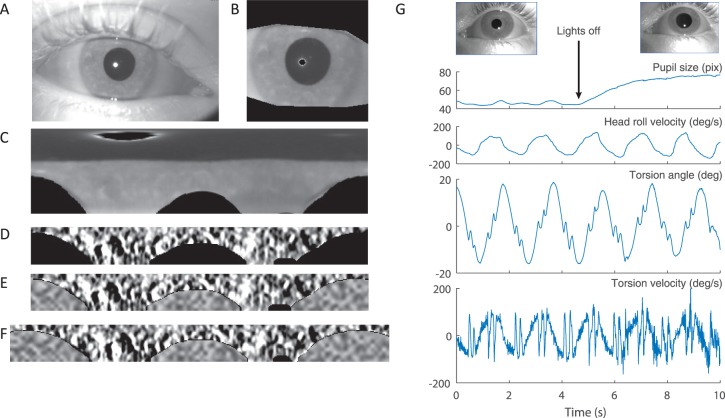
Figure 4.
Iris pattern. (A) Example of image of the eye. (B) Region of interest containing the iris. Eyelids and reflections are masked by black. (C) Polar transformation of the image in panel B. Top corresponds with the center of the pupil, and bottom corresponds with the outer edge of the iris. (D) Iris band extracted from panel C. The iris pattern is filtered to optimize the contrast of the features. (E) Same as panel D but with noise added to replace the masked regions. (F) Reference iris pattern. Note how the reference image expands to both sides, repeating a portion of the pattern. (G) Recoding of torsional eye movements during head rolling while the pupil changes size due to changes in illumination. Top images show images of the constricted and dilated pupils in the light and dark conditions.