Fig 7. The effect of connection noise on synchronization.
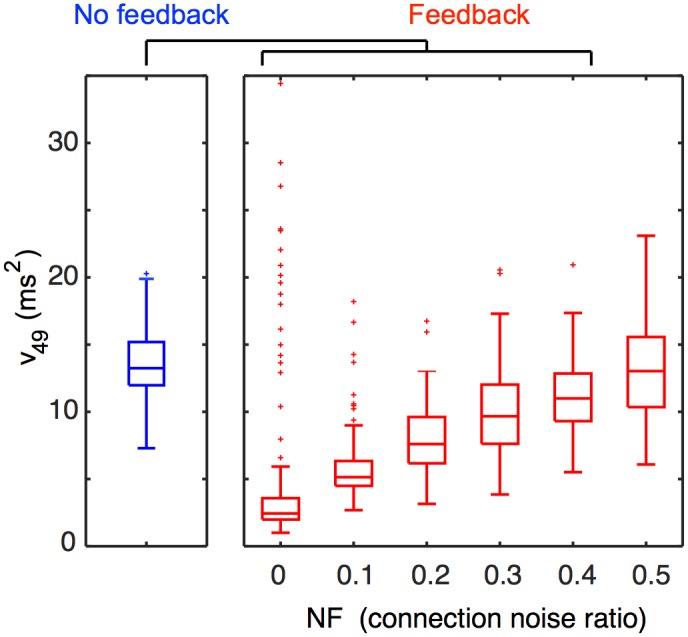
We tested the robustness of the synchronization effect of local inhibition against breakdown of the local network structure by introducing a fraction F of the possible global E-to-I and I-to-E connections into simulation 2. Since there were N times more possible global E-to-I (or I-to-E) than local E-to-I (or I-to-E) connections, NF was the ratio of global to local connections. We computed v 49, the variance of spikes in pool 49, over 100 trials and for a range of values of NF, and made box plots as described in Fig 6. We compared the result to v 49 under conditions of no feedback inhibition (blue). For NF ≤ 0.4, v 49 was significantly different from the model with no feedback with p < 10−9 according to a Wilcoxon rank sum test with a Holm-Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. For NF = 0.5, v 49 was not significantly different with or without feedback inhibition (p > 0.05).
