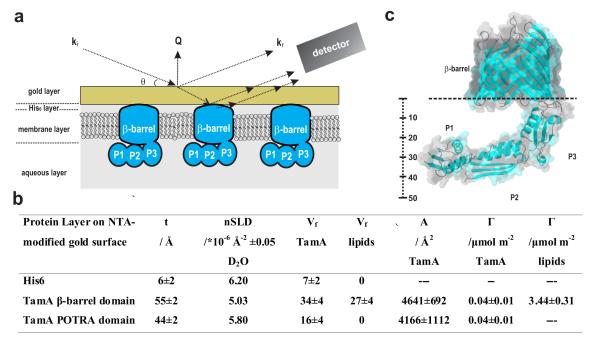
Figure 3.
Structure of TamA in the membrane environment. (a) In the MCNR experimental system, neutrons probe the molecular structure attached to the gold surface, including components of the membrane layer and projections into the aqueous layer. ki represents the incident neutron beam, kr the reflected beam, θ the incident and exit angles of the neutron beam, and Q denotes the scattering vector. (b) The volume fraction (Vf) of both the TamA membrane-embedded (β-barrel) domain, and the POTRA domains in the aqueous layer, as derived from six contrasts (Supplementary Fig. 4b). Assembly of membrane around the TamA β-barrel domain is shown in Supplementary Fig. 5. t: thickness, nSLD: scattering length density, Vf: volume fraction, A: area per molecular, Γ: surface excess. Where applicable, ± denotes the standard deviation. (c) Crystal structure of TamA23 (pdb P0ADE4), highlighting the molecular dimensions of the POTRA domains P1, P2 and P3.