Fig. 6.
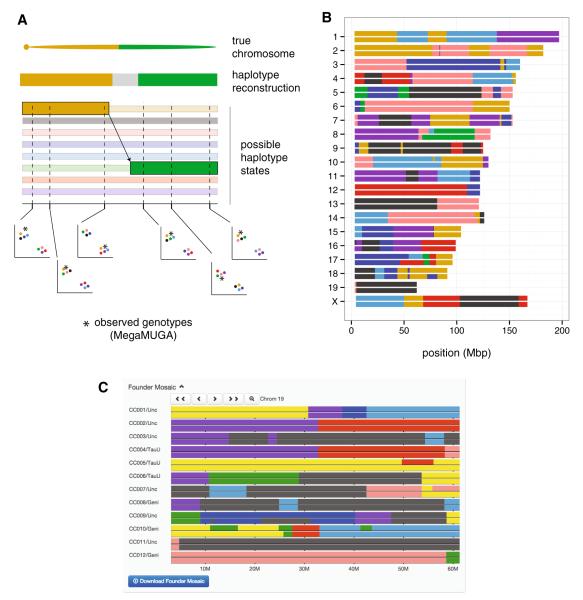
Ancestry inference by a hidden Markov model (HMM) in CC lines. a Schematic of the HMM procedure. (Only the eight homozygous states are shown for simplicity, but the full model has an additional 28 states representing the possible heterozygous combinations.) The true underlying chromosome is recombinant for the A/J and CAST/EiJ haplotypes. Probability of each of eight possible haplotypes is estimated as a function of observed 2D genotyping array intensities (asterisk, unknown sample; colored circles, CC founder strains) along the genome. Information is shared across markers, and the MegaMUGA array is designed to discriminate between all eight founder strains in any 3-marker window. The transition from the A/J to the CAST/EiJ haplotype—representing a crossover event—occurs between the third and fourth markers, but its exact position remains uncertain (gray region) in the final haplotype reconstruction. b Example haplotype reconstruction of a CC line, CC011/Unc, from MegaMUGA genotypes of three obligate ancestors. The line is still segregating for regions on chromosomes 8, 10, 14, 17, and 18. c Screen capture from the interactive Collaborative Cross Viewer showing haplotype mosaics for 12 CC lines in an interval on chromosome 19