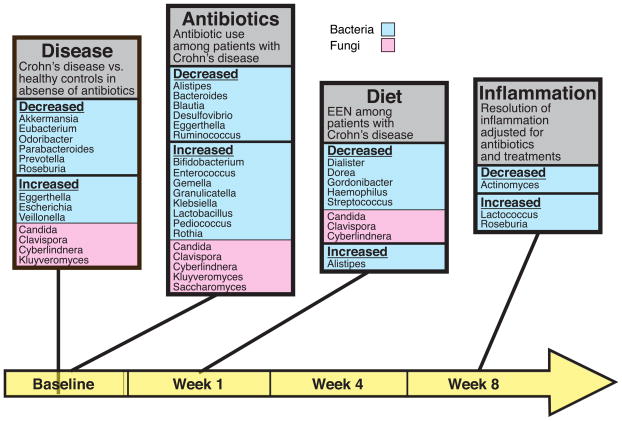
Figure 5.
Bacterial and fungal genera associated with environmental stressors. Microbial genera are shown that differed in four comparisons: Crohn’s disease versus healthy controls at baseline (“Disease”); antibiotic use at baseline in the Crohn’s disease cohort (“Antibiotics”); diet (EEN) or anti-TNF therapy at week 1 (Diet”); and reduction of inflammation or not at the end of the study at week 8 (“Inflammation”). The time line is shown along the bottom (yellow). Bacterial lineages are shown in light blue, fungal lineages in pink. Data for the diagrams are in Tables S1I–L, and S1 N–Q. Taxa shown were significantly associated after adjustment for multiple comparisons for Crohn’s disease versus healthy controls, for antibiotic use comparisons, and for all fungal comparisons. The bacterial taxa shown for the effect of EEN and resolution of inflammation were significant at a nominal p value<0.05 (i. e. without correction for multiple comparisons).