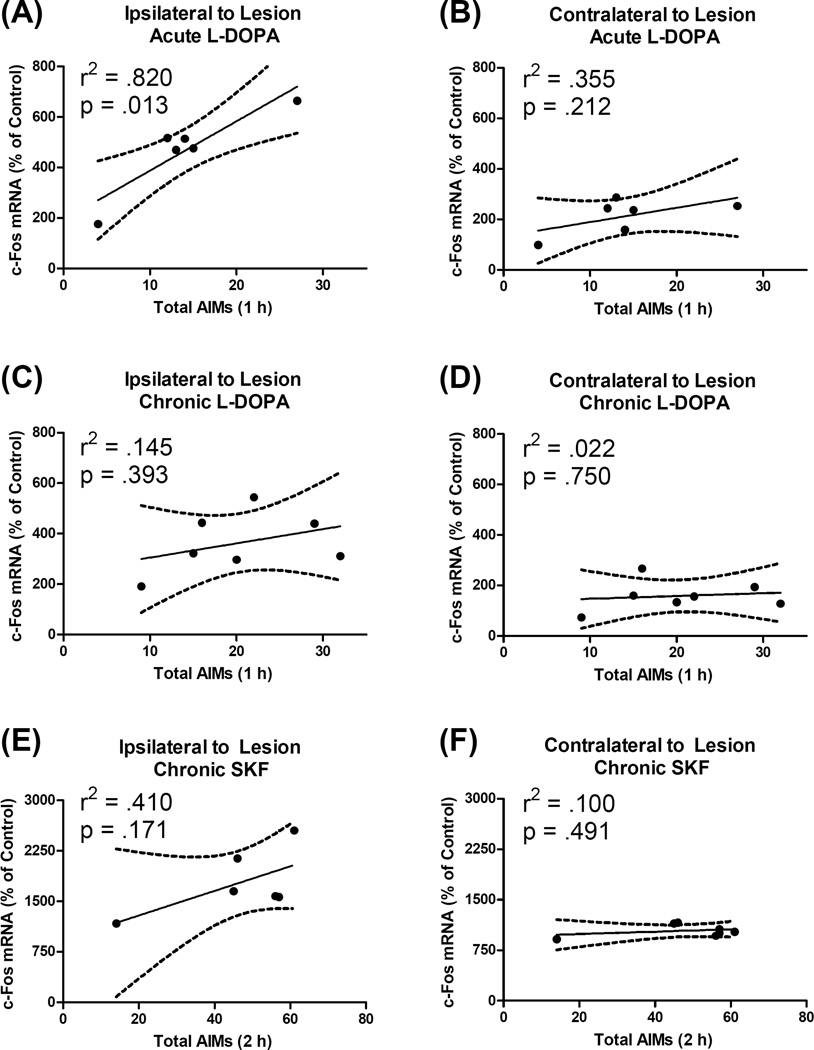
Figure 7.
Correlation between dyskinetic behavior and expression of the immediate-early gene c-Fos in the primary motor cortex (M1). Dyskinesia was scored with the abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) scale while c-Fos mRNA was quantified via polymerase chain reaction. Analyses were performed only on rats that had a (unilateral) 6-hydroxydopamine lesion and received treatment with L-DOPA or the D1 agonist SKF81297 (SKF). Data points reflect individual rat scores. The solid line is the least squared regression line while the dashed line signifies the 95% confidence interval for the slope of the regression line. (A–B) Acute L-DOPA: Previously drug-naïve rats were given their first dose of L-DOPA (6 mg/kg) and tissue was harvested 65 min later. (C–D) Chronic L-DOPA: Rats were treated daily for 15 d with L-DOPA 6 mg/kg and tissue was harvested 65 min after final injections. (E–F) Chronic SKF: Rats were treated four times with SKF 0.8 mg/kg over an 8 d period and tissue was harvested 120 min after final treatment. Note that the axes in panels E–F differ from the axes in panels A–D.