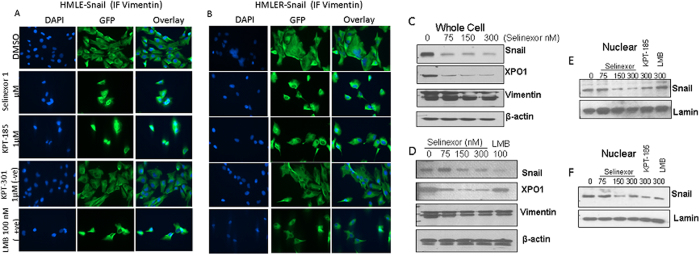
Figure 3. Molecular analysis of SINE compounds in HMECs.
HMLE-snail and HMLER-snail cells were grown (3000 cells per well) in chambered slides. Cells were exposed to indicated doses of SINE, LMB or KPT-301 as –ve control and immunofluorescence assay was performed a described in methods. (A,B) Immunofluorescence images [40×] showing suppression of cytosolic vimentin upon treatment with the drugs in HMLE-snail and HMLER-snail respectively. (C,D) Western blotting of whole cell lysates from HMLE-Snail (top) and HMLER-Snail (lower) cells exposed to indicated concentration of SINE compounds or LMB for 72 hrs. Blots were probed for CRM1 (Santa Cruz, USA), vimentin (Santa Cruz, USA), Snail (Cell Signaling, Danvers USA) and β-actin (Sigma, USA) as a loading control. (E,F) Nuclear lysates isolated from HMLE-snail (top) or HMLER-snail (bottom) post SINE treatment under similar conditions (for 24 hrs). Blots were re-probed with lamin for nuclear loading control. Note: in both cellular models, there is suppression of nuclear snail protein by selinexor and +ve control KPT-185 or LMB. Blots representative of three independent experiments.